You Must Know the Difference Between a Fillet and Chamfer
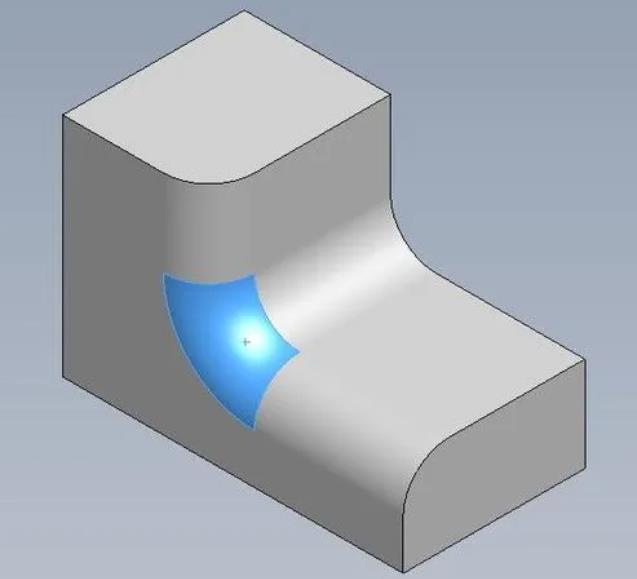
Fillets and chamfers are two distinct approaches to shaping the meeting edges of two surfaces on a part. Their purpose is to alleviate the presence of sharp edges and corners. A chamfer achieves this by replacing the abrupt change in…
