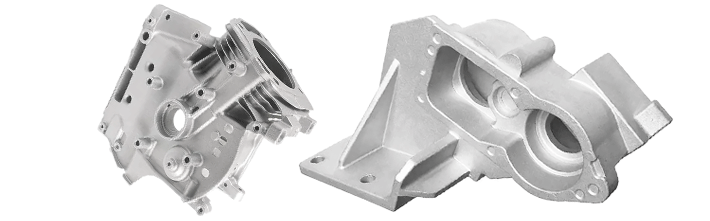
High pressure Die casting
High pressure Die casting
We provided best services to all customers.
We offer first-class high-pressure die-casting services for your parts. You get high-quality, fine finish, and precisely sized parts at competitive prices.
Start Quote
Promise: All files are secure and confidential.
What is high-pressure die casting?
High-Pressure Die-casting is the most common process for metal massive production. In simple terms, melt the metal or metal alloy, and inject the liquid metal into a mold with pressure. The metal solidifies and ejects it. Then we have the product.
Compared with other processes, high-pressure die casting saves material costs, and it can handle relatively complicated designs. Typical casting molds last dozens of thousands to hundreds of thousands of times injections. The unit cost of a product is low.
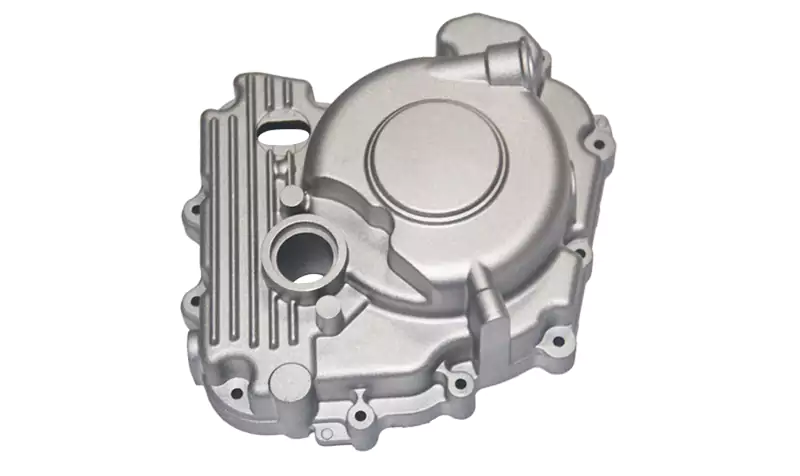

Type services
We use two different systems according to the needs of different products: hot chamber system and cold chamber system. The hot chamber system is used for alloys with lower melting points, such as zinc, tin and lead. Cold chamber die casting machines are used for alloys with high melting temperatures, including aluminum, brass and magnesium.

Hot chamber system
Hot chamber die-casting machines are used for alloys with lower melting points. The molten metal flows into the injection chamber through the inlet, and the hydraulically driven plunger forces the molten metal through the gooseneck channel and into the mold.

Cold chamber system
Cold chamber die-casting machines are used for alloys with high melting temperatures. The molten metal is still kept in an open insulated tank. These alloys cannot be cast in hot chamber die-casting machines because they will damage the pumping system.
Relative services
Difference
Like many things, both hot chamber and cold chamber die casting have their pros and cons. The choice of the correct machining method depends on whether the project is a one-off part development, the application scenario of the final product, which material can meet the customer’s needs, and so on. The differences between the two are now listed for reference.
| Hot chamber system | Cold chamber system | |
|---|---|---|
Processed material |
Low melting temperature alloy(Zinc, Magnesium alloys), max temp 450°C. | High melting temperature alloy(Aluminum, Brass Alloys) , max temp 600°C |
Equipment |
Low Clamp force | High Clamp force |
Molten metal enters |
Sprue bushing (in the cover die) | Injection sleeve |
Cycle times |
400 to 900 shots per hour | 50 to 90 shots per hour |
Parts |
common density and precison | High density parts, higher precision |
Automation |
Easier to automate | More manual labor intensive |
Tooling life cycle |
Longer | relatively short |
Tooling material |
cast iron or tool steel | tool steel |
Cost |
Lower machine and die costs. | Higher machine and die costs. |
Capabilities
Equipment
Hot chamber system: clamp force up to 400 tons
Cold chamber system: clamp force up to 800 tons
Tolerances
Product: Heavily depending on the part type and the size of the part, typically +/- 0.1mm or +/-0.04 inch
Tooling tolerance: typically +/- 0.01mm or +/-0.004inch
Mold Life Cycle
Typically 30,000~50,000
Leading Time
Tooling: 35 days
Casting: 5~7 days
Material
Aluminum Alloy: ADC7,ADC10, ADC12,ADC14 A380, A360, A353
Zinc Alloy: ZA,ZA12, ZA27, AG-40, AG-41
Magnesium Alloy: AZ91D, AZ80M, AZ31B, AM60B, M2M
Thin wall
Typical: >1.5mm(depend on parts type and size)
Process Cycle
The die-casting process cycle roughly consists of five main stages.





Common Materials
Die casting materials are divided into the following three categories according to the properties of the metal materials used
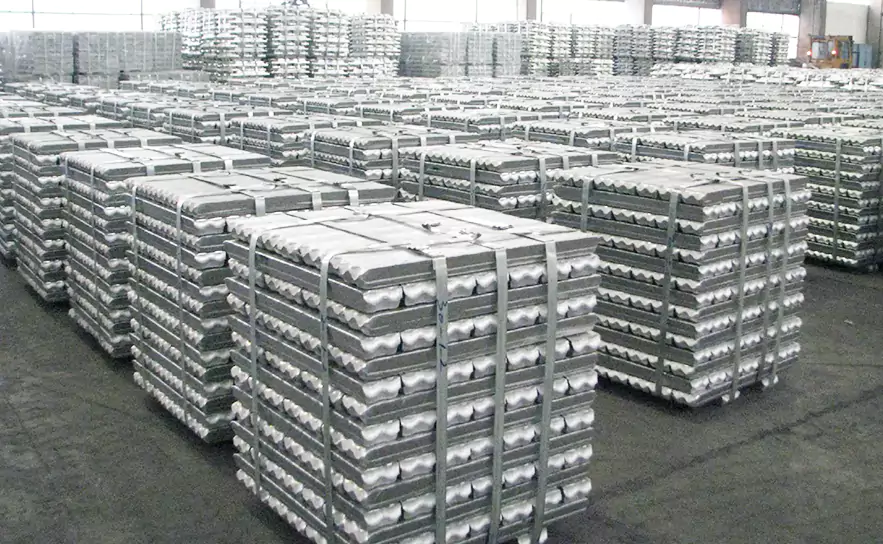

Aluminum alloys
Die-casting aluminum alloys have good performance and process performance, so the die-casting of aluminum alloys has developed rapidly and has been widely used in various industrial sectors.
Material properties:
- Strong and durable: Aluminum alloys are tough, hard, and resist corrosion. For instance, parts made from ADC12 are both sturdy and wear-resistant.
- Efficient heat transfer: Aluminum alloys boast exceptional thermal conductivity. This efficiently spreads and dissipates heat, enhancing parts’ ability to withstand high temperatures. This is particularly crucial in applications like car engines, electric fans, and LED lights, where efficient heat dissipation is essential.
- Easy to mold: Aluminum alloys are highly fluid, allowing them to effortlessly fill molds and solidify rapidly to create desired parts. This ease of molding enables efficient mass production of numerous identical or diverse parts within a short timeframe.
common types: ADC7,ADC10, ADC12,ADC14 A380, A360, A353

Magnesium alloys
Magnesium alloy is an alloy composed of magnesium and other elements. The main alloying elements are aluminum, zinc, manganese, cerium, thorium and a small amount of zirconium or cadmium.
Material properties:
- Light weight, high specific stiffness, high specific strength, strong thermal conductivity
- Good machining performance, good impact resistance and compression resistance
- Good die-casting performance, good dimensional accuracy and stability
- Good regeneration, can be completely recycled
- Low corrosion resistance, flammable and explosive
Mainly used in aerospace, military, automobile, motorcycle and 3C electronic products.
Type: AZ91D, AZ80M, AZ31B, AM60B, M2M

Zinc alloys
Zinc alloy is an alloy composed of zinc and other elements. Often added alloying elements are aluminum, copper, magnesium, cadmium, lead, titanium and other low-temperature zinc alloys.
Material properties:
- Large specific weight; good casting performance, can die-cast precision parts with complex shapes and thin walls, and the surface of the castings is smooth;
- Surface treatment can be carried out: electroplating, spraying, painting, electrophoresis, polishing, water transfer printing, etc.;
- It has good mechanical properties and wear resistance at room temperature;
- Poor corrosion resistance, not suitable for use in high temperature and low temperature (below 0°C) working environment
Mainly used in toys, lamps, decorations, auto parts, mechanical and electrical parts, electrical components and their casings.
Type: AZ91D, AZ80M, AZ31B, AM60B, M2M, etc.
Surface finishes
We have experienced professionals for surface treatment of products.
| Name | Description | Materials | Color | Texture | More |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sand Blast | Sandblasting is a method that uses high-speed sand flow to clean and roughen the surface of a product. It serves to achieve a specific level of cleanliness and varying roughness on the workpiece surface. | All Metal Materials, Plastic | N/A | Matte | |
| Tumbling | Tumbling is a surface treatment process where materials are placed in a rotating drum or container with abrasive media. The action of tumbling smoothens surfaces, deburrs edges, and improves uniformity. | All Materials | N/A | Smooth, Matte | |
| Anodizing | Anodizing is a surface treatment for aluminum and its alloys. It forms a protective layer that boosts corrosion resistance, wear resistance, and hardness while changing the material’s surface appearance. | Aluminum, Titanium | Clear, Yellow, Green, Blue, Black, etc |
Smooth, matte finish. | |
| Painting | Attach the product to be sprayed onto the rotating bracket, and then secure the bracket on the assembly line. Apply the paint evenly to the product’s surface. This process enhances the product’s tactile feel, but it may be susceptible to scratches. | All Materials | Clear, Yellow, Green, Blue, Black, Multiple | Gloss, semi-gloss, flat, metallic, textured | |
| Powder Coating | Powder coating is a technique for applying dry powder to metal surfaces, typically done electrostatically. The coated metal is then cured through heating or ultraviolet light to create a durable and attractive finish. | Aluminum, Stainless Steel, Steel,etc | Custom | Gloss, matte or semi-gloss | |
| Electroplating | Electroplating serves functional, decorative, and corrosion-related purposes, finding widespread use across various industries. For instance, the automotive sector often employs chrome-plating on steel automobile parts. | Aluminum, Steel, Stainless Steel | Gold, Silver, Nickel, Copper, Brass, Zinc, Chrome | Smooth, glossy finish | |
| Electroless Plating | Electroless plating is a chemical process depositing metal onto a substrate without an external electrical current. It involves a catalytic reaction between the substrate and a metal ion solution, creating a uniform and adherent coating. | Metal, Plastic | Gold, Silver, Nickel, Copper, Brass, Zinc, Chrome | Smooth, glossy finish |

Advantages and Disadvantages
High-intensity pressure and speed to produce precise, cost-effective metal castings, is ideal for those looking to manufacture large numbers of identical components, but it has some drawbacks due to its inherent process limitations.
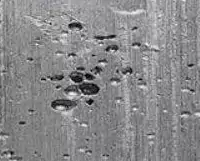
Common Defects
Each process has its own limitations, and it is impossible to have a perfect processing method. When we enjoy the advantages of mass-produced products at low prices, we must also be aware of its common problems. Therefore, choosing which method to use is a matter for us to fully communicate with customers in advance and plan carefully.
General Workflow of Die casting
1. Stp File && Information Sent
2. Quotation


3. Customer place an order
4. We send detail DFM

5. Make the mold
6. T0 (first time test molding)

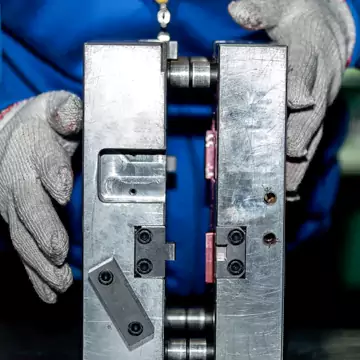
7. T1 (second test molding)
8. Check before acceptance
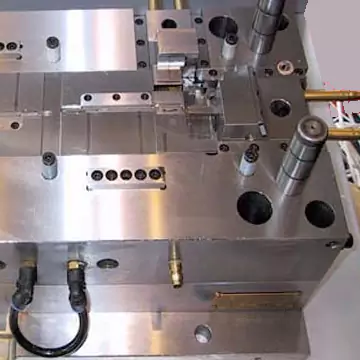

9. Manufacturing
Frequently Asked Questions
Currently, we don’t provide design services, just focus on CNC machining. Although we do have engineers capable of making CAD designs, designing involves intensive knowledge in the field of the product required. Our specialty is converting a design to real not converting an idea to a design.
Yes, we are happy to help you with our knowledge of materials. Please send us the information, we will arrange for engineers to sort it out.
Yes, we do. We manufacture gear, worm, helical gear and some bevel gear in our CNC machining service.
No, we don’t manufacture wood product.
We don’t do 3D print ourself, if you need them, we can outsources for you.
Yes, we do. We do part marking with silk screening, laser engraving, and etching. If you need such service, please send design of the marking in .ai or .dwg form.
Yes we can. 2D drawing contains important information like tolerances, heat treatment, surface treatment etc. Without we will following ISO2768 medium for metal parts and ISO2768 coarse for plastic parts as default, and no heat treatment, no surface treetment, unless otherwise claimed.
The answer is case by case. It depends on if we have the assembly equipments and environment. If it is a simple assembly and we have the equipments, we will offer assembly service.
Stp file is an standard 3D file that all CAD and CAM programes (Proe, UG, Solidworks etc.) can open and convert to. If you only have CAD files with other file extension, send to us, we can covert it to stp file.
Related Blog
Automotive Die Casting and Casting Aluminum Alloys
Aluminum alloy has a series of excellent performance and highly efficient energy saving and environm…
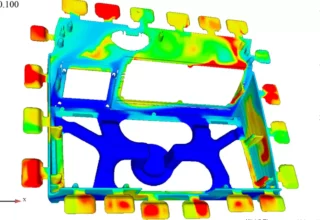
Minimizing Defects in High Pressure Die Casting
Simulation in HPDC 1. Overview of Simulation Software 2. Identifying Defects through Simulation 3. O…
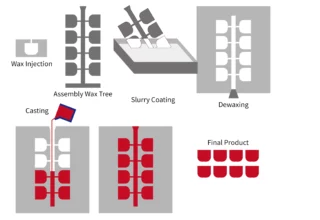
Investment Casting vs Die Casting
Table of Contents Investment Casting Steps of the Investment Casting Process Creating the Wax Patter…