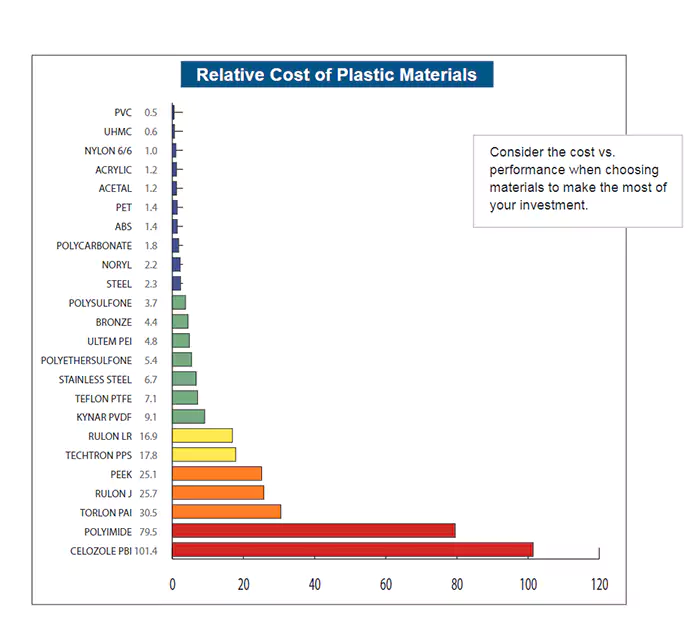
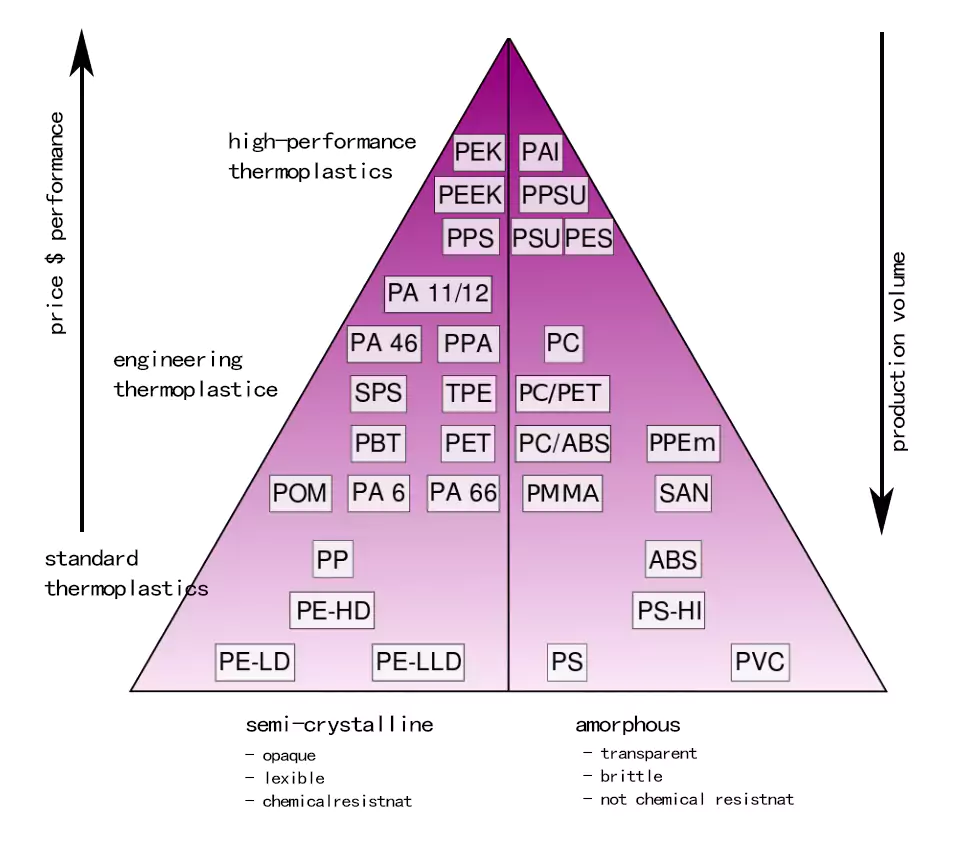
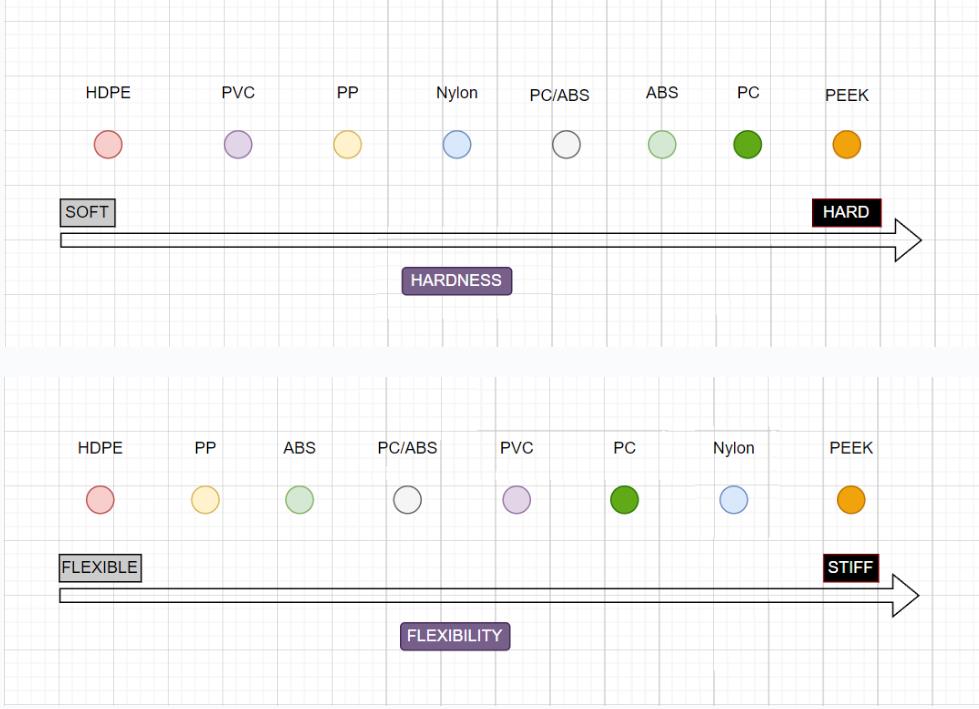
We provide instant quotes for more than 200 kinds of plastic and compare the prices of different processing materials for you.

ABS
ABS is a copolymer made up of three monomers: acrylonitrile, butadiene, and styrene. The combination of these monomers provides ABS with a unique set of properties, including high impact resistance, good heat resistance, and excellent dimensional stability.
| Mechanical properties | |
|---|---|
| Ultimate tensile strength | 27.6 – 55.2 MPa |
| Yield strength | 18.5 – 51 MPa |
| Young’s modulus | 1.1 – 2.9 GPa |
| Elongation at break | 10 – 50 % |
| Hardness | 5.6 – 15.3 HV |
| Thermal properties | |
|---|---|
| Maximum service temperature | 61.9 – 76.9 °C |
| Thermal expansion coefficent | 84.6 – 234 10^-6/ºC |
| Thermal conductivity | 0.188 – 0.335 W/(m⋅°C) |

PMMA
PMMA also known as acrylic, is a tough and transparent material that resists UV radiation and weather. It can be easily colored, shaped, and used for various applications in construction due to its attractive appearance.
| Mechanical properties | |
|---|---|
| Ultimate tensile strength | 55 – 83 MPa |
| Yield strength | 64 -80 MPa |
| Young’s modulus | 2.76 – 3.3 GPa |
| Elongation at break | 3 – 6.4 % |
| Hardness | 64 – 105 HRM |
| Thermal properties | |
|---|---|
| Maximum service temperature | 70 – 80 °C |
| Thermal expansion coefficent | 50 – 90 10^-6/ºC |
| Thermal conductivity | 0.19 – 0.2 W/(m⋅°C) |

PE
PE (Polyethylene) is a popular thermoplastic polymer known for its exceptional properties. This lightweight, durable, and versatile material is widely used in various applications, as it can be easily processed into different shapes and sizes.
| Subtypes | Ultimate tensile strength | Yield strength | Young’s modulus | Elongation at break | Hardness |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| HDPE | 22.1 – 31 MPa | 26.2 – 31 MPa | 1.07 – 1.09 GPa | 500 – 700 % | 7.9 – 9.9 HV |
| UHMW-PE | 38.6 – 48.3 MPa | 21.4 – 27.6 MPa | 0.894 – 0.963 GPa | 200 – 500 % | 3.4 – 8.3 HV |
Nylon
Nylon, a synthetic thermoplastic polymer, requires careful consideration during machining to avoid overheating, which can lead to issues like melting, warping, or damage.
| Subtypes | Ultimate tensile strength | Yield strength | Young’s modulus | Elongation at break | Hardness |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Nylon 6 | 64.7 – 79.1 MPa | 51.2 – 63.8 MPa | 1.58 – 1.97 GPa | 200-300 % | Shore D70 |
| Nylon 6 30% GF | 113 – 138.1 MPa | 111 – 137 MPa | 6.5 – 8.1 GPa | 2.81 – 4.05 % | Shore D92 |
| Nylon 66 30% GF | 90 MPa | 90 MPa | 5 GPa | 10 – 14 % | Shore D76 |
| Nylon 6 FR | 82 MPa | 82 MPa | 3.8 GPa | 3 % | Shore D83 |
| Nylon 12 | 80 MPa | 80 MPa | 1.9 GPa | 200% | Shore D78 |
| Nylon 66 | 76 MPa | 50 – 80 MPa | 1.85 GPa | 50% | Shore D82 |

PEEK
PEEK (Polyetheretherketone) is a unique engineering plastic known for its outstanding properties, including high-temperature resistance, self-lubrication, ease of processing, and exceptional mechanical strength.
| Mechanical properties | |
|---|---|
| Ultimate tensile strength | 70.3 – 103 MPa |
| Yield strength | 87 – 95 MPa |
| Young’s modulus | 3.76 – 3.95 GPa |
| Elongation at break | 30 – 150 % |
| Hardness | 26.1 – 28.5 HV |
| Thermal properties | |
|---|---|
| Maximum service temperature | 239 – 260 °C |
| Thermal expansion coefficent | 50 – 60 10^-6/ºC |
| Thermal conductivity | 0.24 – 0.26 W/(m⋅°C) |

PC
Polycarbonate is a strong and tough plastic with flame retardant and antioxidant properties. It has excellent impact strength, transparency, and mechanical properties.
| Mechanical properties | |
|---|---|
| Ultimate tensile strength | 60 – 72.4 MPa |
| Yield strength | 59- 70 MPa |
| Young’s modulus | 2 – 2.44 GPa |
| Elongation at break | 50 – 120 % |
| Hardness | 17.7 – 21.7 HV |
| Thermal properties | |
|---|---|
| Maximum service temperature | 101 – 144 °C |
| Thermal expansion coefficent | 120 – 137 10^-6/ºC |
| Thermal conductivity | 0.189 – 0.218 W/(m⋅°C) |
PP
PP (Polypropylene) boasts remarkable chemical resistance, a high melting point, and low density. When machining PP using CNC, it’s crucial to use a sharp cutter with a high front angle and a low cutting speed. These measures prevent the material from overheating and melting.
| Subtypes | Ultimate tensile strength | Yield strength | Young’s modulus | Elongation at break | Hardness |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PP Homopolymer | 19 – 30 MPa | 0.7 – 1.2 GPa | min. 50 % | ||
| PP | 23 – 33 MPa | 30 – 32 MPa | 0.9 – 1.6 GPa | 8 – 12 % | 65 – 102 HRR |
| PP+GF(30%) | 68 – 85 MPa | 6.5 – 7 GPa | 2.1 – 3.4 % | 110 HRC |

PET
Polyethylene terephthalate (PET), a thermoplastic material, is a viable option for CNC milling and lathing processes due to its good machinability and versatility. With proper tooling and cutting parameters, PET can be easily shaped and formed, making it ideal for creating prototypes, custom parts, and containers through CNC machining.
| Mechanical properties | |
|---|---|
| Ultimate tensile strength | 50 – 90 MPa |
| Yield strength | 47 – 90 MPa |
| Young’s modulus | 2 – 3 GPa |
| Elongation at break | 20 – 300 % |
| Hardness | 80 – 96 HRM |
| Thermal properties | |
|---|---|
| Maximum service temperature | 60 – 115 °C |
| Thermal expansion coefficent | 40 – 60 10^-6/ºC |
| Thermal conductivity | 0.15 – 0.28 W/(m⋅°C) |

PEI
PEI (Polyetherimide) is a tough and durable material known for its high melting point and abrasive characteristics. By utilizing specialized cutting tools and techniques, it can be effectively cut and shaped to produce high-quality parts with precise tolerances.
| Subtypes | Ultimate tensile strength | Yield strength | Young’s modulus | Elongation at break | Maximum service temperature |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PEI Ultem 1000 | 125 MPa | 125 MPa | 3.1 – 3.3 GPa | 12 – 35 % | 170 °C |
| PEI Ultem 2300 30% Glass Filled | 135 MPa | 135 MPa | 5.3 GPa | 4 % | 170 °C |

POM
POM (Polyoxymethylene) is a thermoplastic material renowned for its high stiffness, low friction, easy cutting, and excellent dimensional stability. However, machining POM can be challenging due to its high melting point and susceptibility to chipping or cracking if the cutting parameters are not carefully controlled.
| Subtypes | Ultimate tensile strength | Yield strength | Young’s modulus | Elongation at break |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Acetal Copolymer(POM-C) | 60 – 70 MPa | 60 – 67 MPa | 2.5 – 2.7 GPa | 30 – 32 % |
| Acetal Copolymer (POM-C) FDA | 70 MPa | 66 – 70 MPa | 2.8 – 3 GPa | 32 – 40 % |
| Acetal Homopolymer (POM-H) | 60 – 89.6 MPa | 48.6 – 72.4 MPa | 2.5 – 4 GPa | 15 – 75 % |
| Acetal Copolymer (POM-C) ESD | 39 MPa | 45 MPa | 2.5 – 2.7 GPa | 40 – 50 % |

PVC
PVC is strong, durable, and resistant to chemicals, weather, and fire. However, machining it can create harmful dust and fumes that may be unsafe for workers. To keep workers safe, use proper safety equipment and ventilation during the process.
| Mechanical properties | |
|---|---|
| Ultimate tensile strength | 46 – 58 MPa |
| Yield strength | 53 – 58 MPa |
| Young’s modulus | 2.18 – 3.41 GPa |
| Elongation at break | 25 – 80 % |
| Hardness | 13.7 – 16.6 HV |
| Thermal properties | |
|---|---|
| Maximum service temperature | 85 – 100 °C |
| Thermal expansion coefficent | 112 – 149 10^-6/ºC |
| Thermal conductivity | 0.133 – 0.144 W/(m⋅°C) |

PTFE
When machining PTFE, using the right cutting tools is crucial because PTFE has a low friction coefficient, which can lead to overheating and deformation of the tool. To overcome this, carbide cutting tools are commonly employed as they are durable and can withstand heat effectively.
| Mechanical properties | |
|---|---|
| Ultimate tensile strength | 25 – 31 MPa |
| Yield strength | 14 – 41.4 MPa |
| Young’s modulus | 0.39 – 2.25 GPa |
| Elongation at break | 300 – 450 % |
| Hardness | 50 – 65 Shore D |
| Thermal properties | |
|---|---|
| Maximum service temperature | 250 – 270 °C |
| Thermal expansion coefficent | 7 – 20 10^-6/ºC |
| Thermal conductivity | 0.23 – 0.5 W/(m⋅°C) |
How to Make the Right Choice
There are several important elements to take into account when choosing plastic materials for CNC machining to make sure the finished product fulfills your expectations. Here are some factors to take into account when choosing a plastic material:
Mechanical Properties: Select a plastic material with the proper mechanical qualities, such as strength, hardness, and wear resistance, depending on the project’s requirements. ABS, polyurethane, and other popular polymers have good mechanical qualities.
Chemical Resistance: To avoid corrosion or distortion, you must use a plastic material with strong chemical resistance if your parts must come into contact with chemicals. Both polypropylene and polyethylene can withstand chemicals well.
Temperature Resistance: You must select a plastic material that can tolerate the necessary temperature range if your component will be used in a high- or low-temperature environment. For instance, PA66 (nylon 66) is well suited to withstand high temperatures.
Electrical Properties: You may want to use a plastic material with good insulating characteristics, such as polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE), for applications that call for effective electrical insulation.
Transparency and Color: Choose a transparent or tinted plastic material, like polycarbonate (PC), if you require a specific color or level of transparency for a component.
Cost considerations: The price of various plastic materials will differ, therefore you must choose the best material in accordance with your project budget.
Machinability: Consider the material’s machinability, taking into account its cutting capabilities, abrasion resistance, and ease of shaping into the appropriate shape.
Environmental considerations: With more and more projects focusing on the environment, you can minimize your environmental impact by choosing plastic materials that are recyclable or biodegradable.
Reference
Plastic Standard and other
Plastic materials are often regulated and standardized to ensure their safety, quality, and environmental impact. One of the well-known standards organizations that sets standards for plastic materials is the International Organization for Standardization (ISO).
Other
Materials are an essential basic capability in the industry, and their development can promote technology and innovation and society’s development. The current trend of material development is to be more environmentally friendly and energy-saving.
Related Blog
Automotive Die Casting and Casting Aluminum Alloys
Aluminum alloy has a series of excellent performance and highly efficient energy saving and environm…
12 Design tips for plastic injection parts
Choose the right material Choosing the right plastic material for injection molded parts can be tric…
Plastic Injection Molding Materials
Table of Contents Features And Differences Among Materials Crystalline plastics Non-crystalline plas…

“Customers are our partners, so we prioritize their needs.”
— CapableMaching