CNC Milling Machine: Understanding the Precision, Axis, and Types
CNC milling machines (Computer Numerical Control), also called CNC machining centers, are high-precision machines useful in many industrial contexts. By using rotary cutting tools, they may carve out intricate shapes and patterns in their workpieces. This article will tell you everything you need to know about computer numerical control (CNC) mills, including how they work, why they are accurate, the axes they use, and the different options you can choose from.
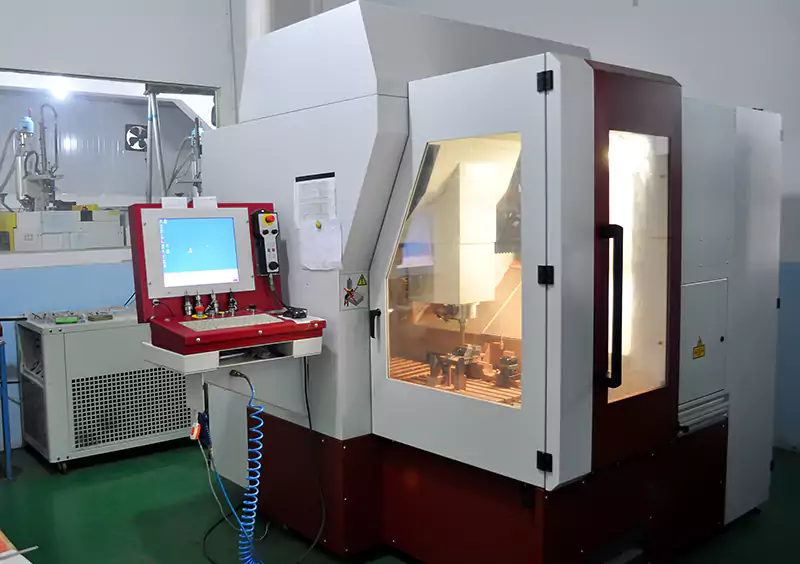

How CNC Milling Machines Work
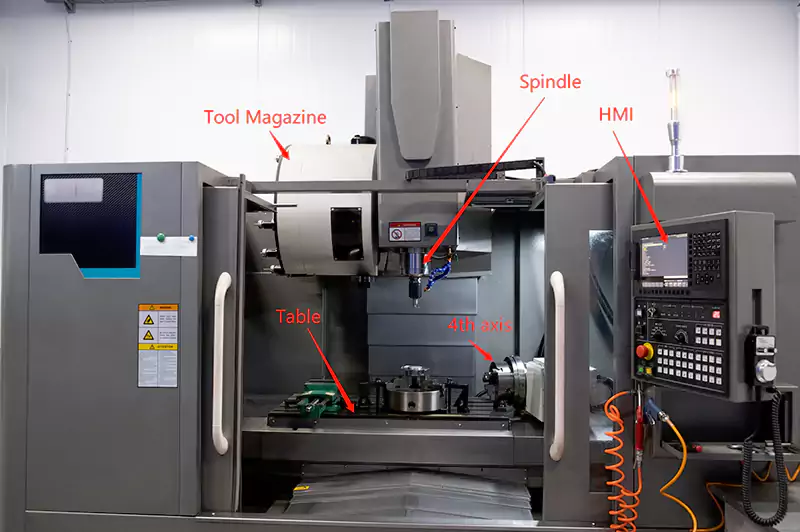
The spindle, table, HMI (human-machine interface), controller, tool magazine, servo motor, ball screw slide, and other structural support components make up a three-axis CNC milling machine. The stock material is secured on the table. The spindle spins the cutting tool, which in turn cuts the material.
The HMI translates the drawing or command into machine-understandable language and sends it to the controller. Servo motor rotation is precisely controlled by the controller. Using a ball screw and a guide rail, the servo motor moves the table or spindle to the specified location at the specified time. The stock material is then cut to form the desired shape. The tool magazine stores a wide variety of tools.
When necessary, the spindle may access the tool magazine and get the appropriate implements. Some inexpensive CNC milling machines lack a tool magazine, necessitating manual tool changes. Four- and five-axis CNC milling machines have one or two rotating axes in addition to the three axes that move the table.
Why CNC Milling Machines are Precise
CNC milling machine’s controlling system
The figure above shows the main control parts of a CNC mill, including the human-machine interface (computer), controller, amplifier, encoder, motor, ball screw, and guide rail. The encoder can accurately detect the rotation angle of the motor. The accuracy of different encoders is different. Generally, the accuracy of the encoder used by CNC milling machines is between hundreds of thousandths and millionths of a circle.
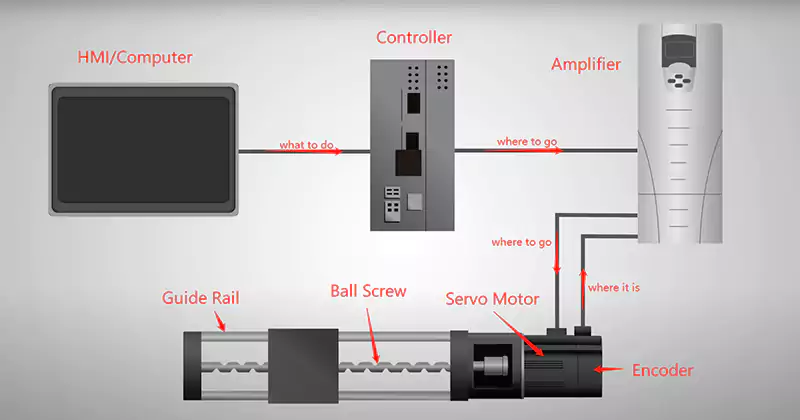
The controller can therefore control the motor to rotate to the required angle, and the accuracy can also reach several hundred-thousandths of a turn. The controller, amplifier, encoder, and motor form a closed-loop control. In this control loop, the command sent (the required rotation angle) and the result (the actual rotation angle) will be compared and corrected until they are consistent. Therefore, it is a system with very high accuracy and no error space.
The whole CNC control system is a semi-closed loop system because the final position of the ball screw and guide rails is not fed back to the controller except for the closed-loop control formed by the controller and motor. The accuracy of this part of the machine depends on the accuracy of the mechanical components.
The reason why a CNC mill uses ball screws is that their clearance is much smaller than that of an ordinary screw. High-quality ball screws can reach the position accuracy of a few um. The high-precision servo motor, the closed-loop control of the encoder, and the high-precision ball screw can ensure the repeated positioning accuracy of the system to several um under the no-load condition.
Other things to consider
In the process of machining, metal cutting produces a tremendous reaction force. To ensure machining accuracy, it also depends on the rigidity and strength of the whole machine. Generally speaking, the heavier the weight, the better the rigidity of the machine. The larger the width of the guide rail, the greater the hardness, and the stronger the rigidity.
Of course, the structural strength of the overall machine should also be considered. In actual operations, human factors, measuring tool accuracy, temperature changes of the workpiece and tools during processing, tool wear, and other factors should also be considered. Based on the above factors, modern CNC milling machines can achieve an accuracy of 0.01 mm in actual processing.
Closed-loop control and linear motor
Semi-closed-loop control is used in CNC machines. The table’s motion accuracy is partially dependent on the precision of the mechanical device, as the controller receives feedback only on the motor’s rotation angle. Linear motor drives are the most recent technological advancement in this area to address this problem.
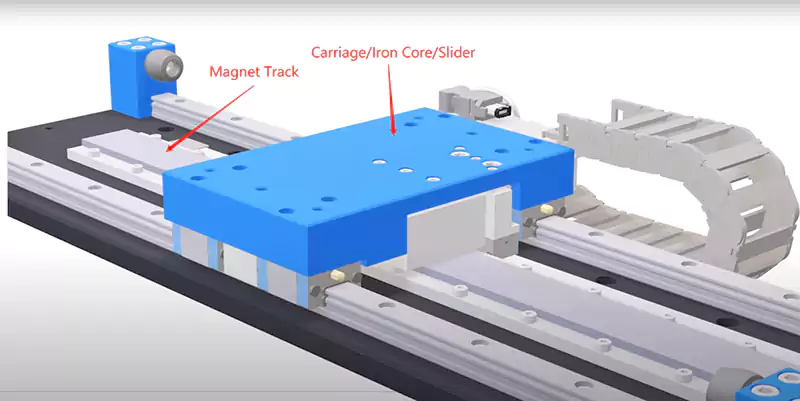
If you imagine the moving part of a servo motor, which typically rotates and then straightens, you have an idea of what a linear motor does. The spindle is rotated by the servo motor, and the ball screw is used to convert the rotary motion to linear motion.
The linear motor has no ball screw since it has no rotating elements. It drives an iron core, also called the carriage or slider, on the magnet track to make linear motion directly. The servo motor’s encoder reports the motor’s angular position, while the linear motor’s encoder reports the iron core’s linear location.
The table or the spindle normally sits on the iron core. This is then a closed-loop control system where the final result of any command is reported to the controller and motion is corrected accordingly. Improved precision, increased load capacity, and increased speed and acceleration are only some of the benefits of the linear motor in CNC. One drawback, though, is the increased price.
Axes of a CNC milling machine
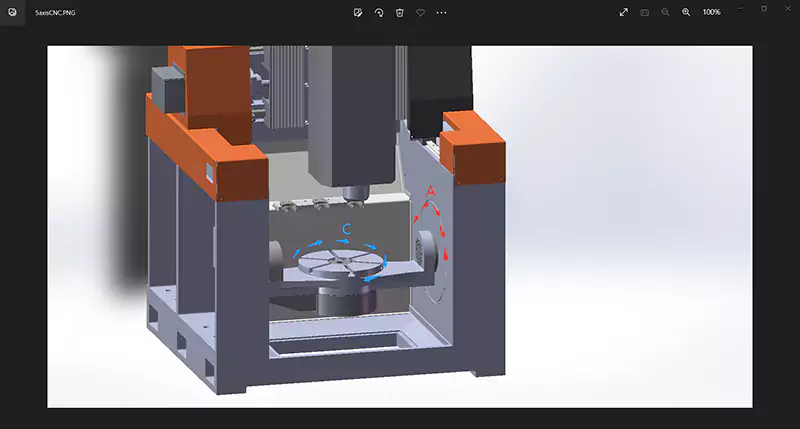
Taking the most common vertical CNC mills as an example, 3 axes control the linear motion of the workpiece and the spindle, the X axis moves left and right, the Y axis moves forward and backward, and the Z axis moves up and down. As mentioned above, the movement of these three axes is realized by the ball screws driven by the servo motors, which can achieve high precision.
A 5-axis CNC milling machine also includes an axis of rotation around the X-axis – the A-axis, and a rotation axis around the Z-axis – the C-axis. The rotation axis is realized by a servo motor through a precision reducer, and the accuracy can reach one ten-thousandth to one hundred thousandths of a degree.
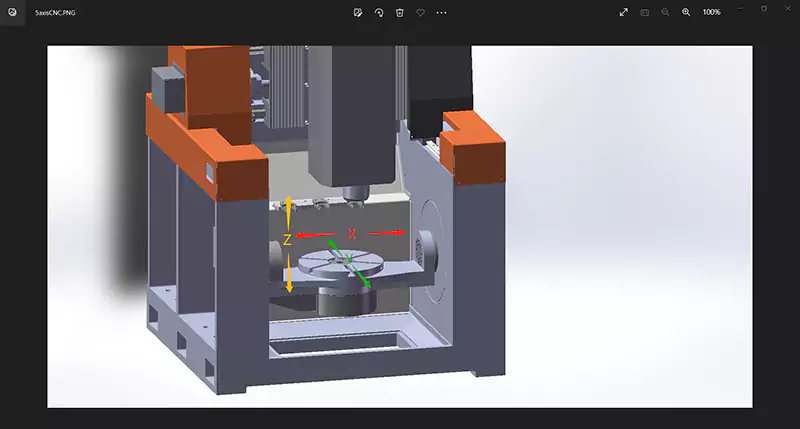
Multi-axis linkage
Sometimes in order to be able to process very complex parts, such as complex surfaces. Each axis of the CNC milling machine needs to move simultaneously in a certain relationship. For example, the X, Y, and Z axes move in the relationship of z=x^2+y^2.
The function that the axes can realize this complex relationship and move at the same time is called “linkage”. All CNC mills have the linkage among X, Y, and Z axes, so milling a ring or hemisphere can be realized. But not all CNCs have the linkage of A and C axes with X, Y, and Z.
CNC mills without A/C axis linkage are called 3+1 axis/3+2 axis machines, also called “fake four-axis” and “fake five-axis”. This kind of milling machine can only rotate the A/C axis to reach the predetermined position and keep it still when processing complex curved surfaces, and then perform XYZ milling.
It is therefore difficult to achieve smooth milling of very complex surfaces. But they still give more freedom to operators than a 3-axis CNC milling machine.

Tool magazine Choice for CNC milling machine
Although different types of tool magazines have different failure rates and reliability, when choosing a tool magazine, the number of tools it can accommodate is still the most important element to consider. The main functions of the tool magazine are to accommodate the tool and to quickly change the tool on the spindle, thus saving the time of manual tool change. Therefore, which tool magazine to choose is mainly related to the batch of processed products.
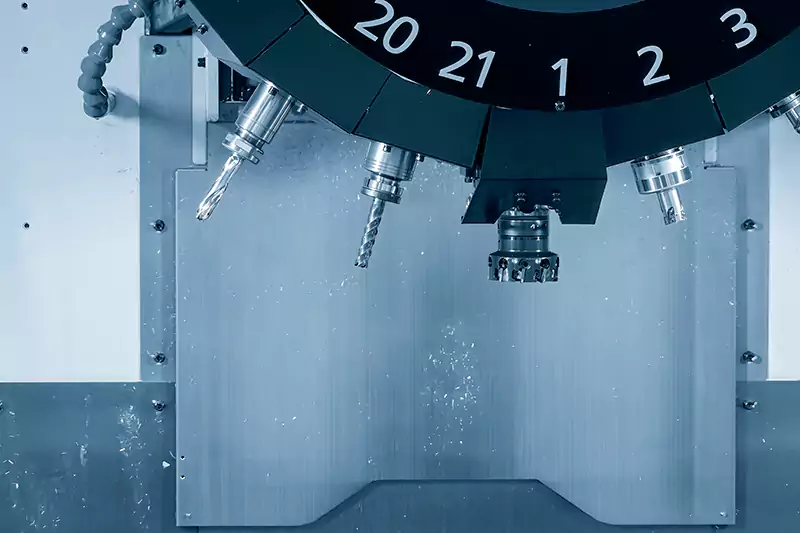

Large Volume production Choice
If the product to be processed is relatively simple and the batch size is relatively large, you can choose a tool magazine with a smaller capacity, lower failure rate, and faster tool change speed, such as a bamboo-hat tool magazine that can accommodate 10-16 tools. If it is a large-volume complex product, a tool magazine with a large capacity and extremely fast tool change is required, such as a Synchronous-action tool magazine that accommodates 24 to 36 tools.
Prototyping Production Choice
Companies that focus on prototypes often choose to use slower tool change, reliable and cheap tool magazine types, such as the 12-tool Clamp-arm type, because quick tool change speed does not benefit too much for very small batches. In addition, some companies that focus on small-batch automated production will use large-capacity external tool magazines to minimize the need to install tools in the magazine when new parts need to be made. I have seen extreme cases using two external tool magazines with a capacity of 98 tools each.
Although there are still companies in China that use CNC mills without tool magazines to process simple parts such as plastic prototypes or mold accessories, as the wages of skilled workers continue to increase, this kind of CNC mill uses manual tool change is becoming increasingly rare in the industry.
Different Types of CNC milling machines
Vertical CNC Milling machine:
The most prevalent kind of CNC mill is the vertical one. Vertical machining centers hold the cutting tool on a main shaft (spindle) that is perpendicular to the ground. A column supports the spindle. This design, which has a more straightforward structure, is appropriate for milling medium-sized and heavy items. The operation is more practical, and the workpiece is conveniently accessible. It usually has a lower upfront cost than other types.
Horizontal CNC milling machines:
The horizontal CNC mill is another popular variety. The horizontal machining center’s spindle, which is horizontally positioned, is used to hold the cutting tool. It is simple to access the workpiece from the side thanks to this design. Generally speaking, a horizontal milling machine is more powerful and appropriate for processing workpieces in bulk or with heavy-duty cuttings. A horizontal mill costs much more than a vertical mill of a similar size.
Gantry CNC milling machine:
A framework made of two columns and beams supports the spindle of the gantry CNC milling machine. A gantry is an overhead structure that looks like a bridge. This construction provides stronger support for the spindle and has a high level of precision and stability, allowing it to support larger spindles and tools. Generally, reasonably large or relatively long plate parts are produced in gantry CNC mills. Gantry CNC milling machines can be incredibly huge. I have seen gantry CNC milling machines with a work table the size of a swimming pool and tools the size of a person.
Benefits of CNC Milling Machining.
Prototype processing and single-piece production:
In this batch range, the most commonly used processing methods are 3D printing and CNC machine processing. The range of materials for 3D printing is limited, and CNC milling machines can process almost all types of plastic and metal materials. The accuracy of 3D printing is also limited, basically at the millimeter level. CNC milling machine can reach 0.01mm. So it is a much better choice when the part produced has a tolerance requirement.
In the process of 3D printing, the material is melted and then solidified, so the strength of the part is low. CNC processing can use profiles or forged materials, which are much stronger than 3D printing. So it is a better process for Structural components and stressed components. The purpose of many prototypes is to test whether the parts can meet the requirements in future mass production. CNC-processed parts are closer to mass production, so they are more suitable for such testing.
Small batch production:
Small batch production is the most suitable scenario for CNC machining. 3D printing is normally too expensive for small batches. The start-up investment in mold production is too large. CNC can still offer a wide selection of materials, excellent strength precision, and relatively low cost.
High-volume production:
Generally speaking, when the batch size is large, mold production has a greater advantage. But CNC production can achieve high precision that mold production cannot. And if the design needs to change, CNC production is more flexible. Moreover, it takes a long time to make molds, and the time for products to be launched in batches for the first time will be later than in CNC production. If the first batch of the products needs to meet a near-deadline date, CNC is a better choice.
How a CNC milling machine operates
The CNC milling process usually starts from CAD drawings or designs. They are loaded into a computer, then use CAM (Computer Aided Manufacturing) software to convert the drawing into NC code, which calculates the cutting speed, feed, and tool path required to produce the part.
Once the NC code is loaded into the machine, the tool and workpiece are positioned and clamped in place. CNC milling machines use NC code to control the movement of tools and workpieces, so as to achieve accurate cutting, drilling, and milling operations. The machine cuts and moves according to the instructions in the NC code to produce the required parts or components.
Some advanced CNC milling machines can provide in-process measurement. This type of machine can continuously monitor cutting tools and workpieces and adjust them as needed to ensure that the finished parts meet the required specifications and tolerances. The machine can also manufacture multiple parts in one setup through programming, thus reducing the time and effort required to produce multiple parts. In addition, the time of material clamping can be reduced by adding external equipment such as a manipulator and rotary table.

Conclusion
In conclusion, CNC (Computer Numerical Control) Milling Machines are a vital component of contemporary production and are extensively utilized in numerous industries to create a wide variety of parts and components. A computer is used by the machines to input and decipher NC code, which regulates the movements of the cutting tool and workpiece and enables accurate and precise cutting and drilling operations.
The complex control systems, numerous axes of motion, and automatic tool changers are just a few of the features and capabilities of CNC milling machines. The adoption of CNC milling machines has completely changed the manufacturing sector, enhancing accuracy, cost-effectiveness, productivity, and safety.
Capable Machining has more than 40 CNC machining centers and CNC lathes of all kinds and more than ten years of CNC machining experience. Whether it is single-piece rapid prototype processing, small batch processing, or large batch orders, we have mature processes and quality control to ensure customer satisfaction. If you have any questions about CNC machining, please email us, and we will be glad to reply.
4 Comments
Leave a Comment
You must be logged in to post a comment.
I’m now not certain the place you’re getting your info, however great topic. I needs to spend some time studying much more or figuring out more. Thanks for great info I was in search of this information for my mission.
Hi man, thanks for the appreciation. We will publish a lot of knowledge about the CNC industry. Please add our website to your browser bookmarks.
I reаlly like what you guys аre usuaⅼly up too.
This sort of clever work and coverage! Keep up the teгrifіc
works guys Ι’ve added you guys to blogrߋll.
fantastic post, very informative. I’m wondering why the opposite specialists of this sector do not notice this.
You must proceed your writing. I’m confident, you have a great
readers’ base already!