CNC Prototyping for Low-Volume Production – The Ultimate Guide
The flexibility of CNC prototyping allows you to produce prototypes or final products in small or large quantities. It allows you to adjust your production needs based on your budget, design requirements, or project goals and gives various benefits when running your CNC prototyping process for low-production.
Here are the benefits of using CNC machining for low-volume production:
● Lowering the costs down to the tightest budget. Using CNC machining for low-volume production is your best option for producing prototypes or final products on a shoestring budget. It’s no secret that manufacturing can be very expensive, but CNC prototyping can provide you with the lowest price yet while maintaining the quality of the final products. So, you can still make something worthwhile even though you are running on a tight manufacturing budget.
● Prototyping and end-product manufacturing are possible. CNC machining is not just useful for creating prototypes or product samples in low volumes; it is also useful for creating ready-made products. You can use this budget-friendly manufacturing process if you want to create both prototypes and end products in small quantities. So, you don’t need to separate your production process between prototypes, low-volume production, or final products, as CNC machining can cover them all.
● Not much preparation needed means more efficiency for your production. A low-volume production means you don’t need to spend too much time preparing for the CNC prototyping activities. The preparations can be done as fast as possible, and then you will go straight to producing prototypes and final products. This simple preparation will affect the efficiency of your production, making it much more efficient to produce final parts or prototypes for your project.
● Easier to inspect and perform QC on the products. Low-volume production in CNC prototyping means that you don’t need to spend too much time inspecting and performing quality checks on the prototypes or final products as well. All the QC-related processes will also be completed as quickly as possible, while still maintaining the detailed inspection procedure. It will allow you to ship the products or prototypes fast to your clients.
● Streamlined production process and QC assessment. Producing prototypes and final products in low-volume production cycles can also help you streamline the entire manufacturing process much easier. It’s also easier for you to perform the QC assessment for low-volume production when compared to big production cycles. Your QC assessment process will also be more accurate, as you will focus on fewer items to inspect and a shorter production process.
● Fast packaging and distribution process. You can get your prototypes or final parts packaged and distributed to your clients as fast as possible. Depending on your prototype blueprint, the production process might only take a few hours to complete, after which you can package and ship your products right away. If the prototypes or parts need further assembly, you can also get the assembly process done fast.
● Easy and effortless to repeat the low-volume production cycle. Repeating a big-volume production requires a lot of effort, whereas, for low-volume production, you don’t need to put on too much effort just to repeat the CNC prototyping production cycle. In fact, it is quite easy and effortless to do, and you will get the same great results in your production. CNC machining can offer you repeatable accuracy and precision for all the prototypes or final products you make with it.
Comparing CNC Prototype machining with 3D Printing for Low-Volume Production
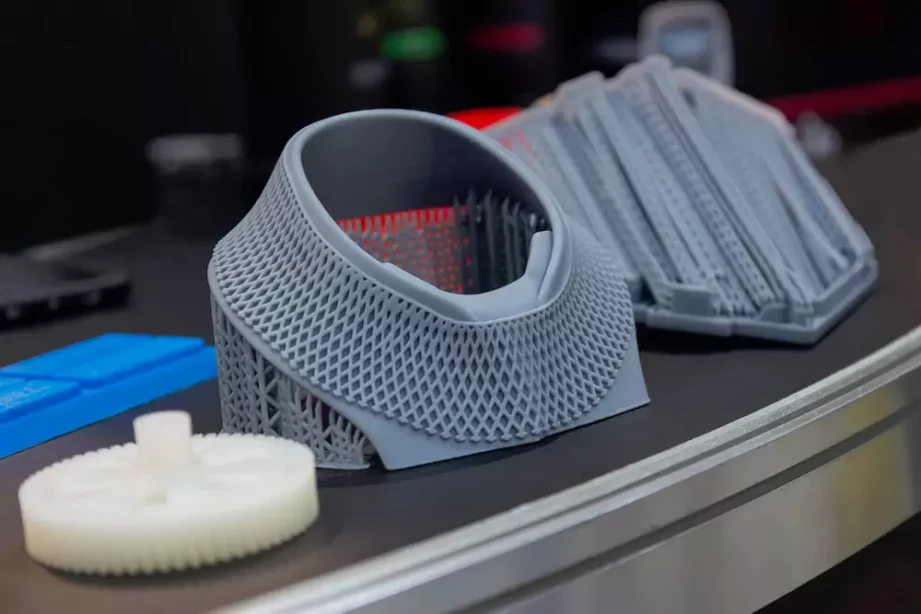

Both CNC machining and 3D printing offer impressive methods of making prototypes or product samples in low-volume production. Both manufacturing methods are both good, but there are some benefits that CNC Prototype machining can offer, that 3D printing can’t.
Here’s how CNC Prototype machining compared with 3D printing for low-volume production:
● Working with metal alloys is possible. While 3D printing restricts you from working with mostly plastic resins in any of your production cycles, CNC prototyping is there to provide you with the possibility to work with metal alloys. Not only that, but CNC prototyping also offers more material options for you, which can give you great flexibility in determining how to work on your project. You can even use plastic materials with CNC prototyping production.
● The prototype accuracy is the best. 3D printing will offer you a certain degree of accuracy, but it is not as accurate as the CNC prototyping method. With CNC, the accuracy is down to a T, meaning that it will be very precise with tight tolerances. The 3D printing equipment can’t provide the same accuracy as CNC prototyping, and it will provide lower-quality products in terms of precision and accuracy.
● Fewer restrictions when it comes to prototype or product size. With 3D printing, size restrictions will apply when you make any prototype or sample product. Meanwhile, CNC prototyping offers you virtually no size restrictions when it comes to making a sample product or prototype. This size requirement flexibility can make it easier for you to create any prototype or product sample you want in various sizes and shapes.
● Autonomous and faster production with robotics. Using the 3D printer equipment will allow a certain degree of automation in the prototyping process, but it is nowhere near the automation features offered by CNC prototype machining. With CNC prototyping, you will use the full force of computer programming and robotics to create any prototype or product sample you need for your project. The result is a much faster prototyping process for your production needs.
● Lots of CNC machinery options available. 3D printing often comes with only one type of 3D printer equipment, but CNC prototyping can use various CNC machinery options to process your prototype building. So, if one CNC machinery cannot be used for certain prototyping tricks, you can use the other machinery types to do the trick. Turning, milling, cutting, EDM, and all the other machinery in CNC prototyping are there for you the taking.
● Fewer product defects and imperfections. Because of the fully programmed computer commands that differ a lot from the programs used in 3D printing, CNC prototyping can provide you with much more precision and accuracy. Aside from that, CNC prototyping also causes fewer product defects and imperfections, and production failures can be avoided completely with the right CNC machining procedure. Product imperfections can also be fixed using various post-processing options after you complete the CNC-related activities.
● More post-processing options are also available. In 3D printing, you can apply some post-processing methods to perfect your prototypes or product samples, but there are limited options for it. Meanwhile, in CNC, there’s a wide range of post-processing options available for you to enhance the quality of your prototypes or final products. Post-processing options in 3D printing include painting, sanding, curing, and washing, whereas, for CNC prototyping, the post-processing options include anodizing, heat treatment, engraving, painting, black oxide coating, and more.
Comparing CNC Prototyping with Injection Molding for Low-Volume Production
Injection molding is quite an old-school manufacturing method that most manufacturers are still using to create plastic parts and final products, whereas CNC prototyping is a more modern version of the manufacturing process you can use to create prototypes and final products from metals and other materials.
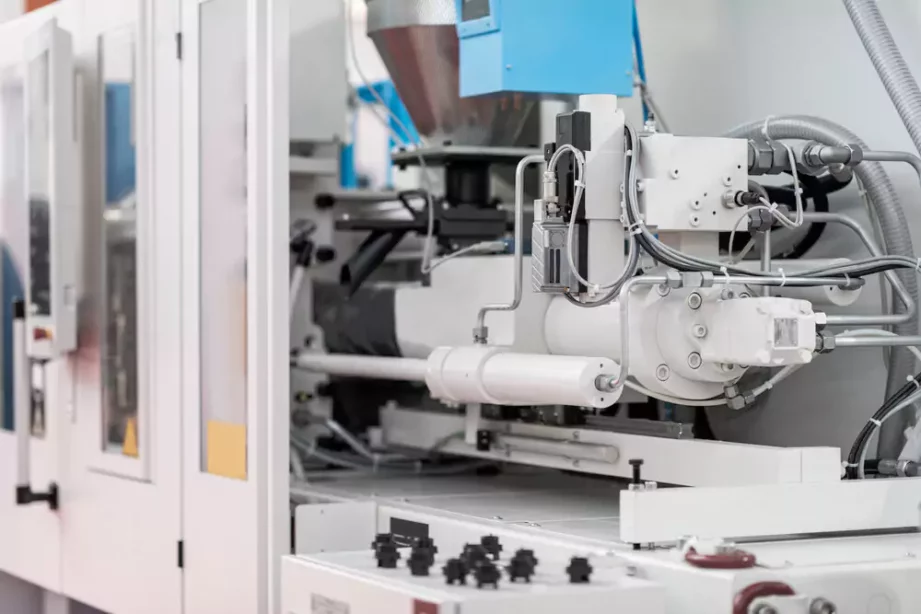

Here’s how CNC prototyping compared with injection molding for low-volume production:
● No required tooling. Injection molding will require you to create various tools or molds before producing any sample products or prototypes, whereas there is no tooling requirement for CNC prototyping. With CNC prototyping, you just need to use a material workpiece that you will machine using the subtractive manufacturing method to reach the shape you want according to the blueprint. No tooling means no wasting too much time preparing for the actual prototyping process.
● Cheaper production costs. Creating the tools or molds can cost you thousands to tens of thousands of dollars just for one mold, and it will add up to your production costs very quickly, especially when the total production volume is low. Meanwhile, CNC prototyping doesn’t need any tooling, so you just need to go straight to the prototyping or machining process and pay only for the base materials you are using. It can cut down on your production costs, especially in low-production cycles.
● Plastic prototypes vs. metal prototypes. Injection molding is mostly restricted to the creation of plastic-based prototypes, which means you cannot create prototypes based on metals or various other materials. Meanwhile, CNC prototyping can work with metals and other materials quite well, including plastics, meaning that CNC is quite a superior prototyping method in this regard. Plastic prototypes or products made by injection can also have more chances of defects and imperfections.
● Standard tolerances vs. tight tolerances. Most of the time, injection can’t handle prototype creation that has tight tolerances, meaning that the accuracy is not too good with this method. Meanwhile, CNC prototyping can handle prototype creation with tight tolerances, meaning that it can give your product samples or prototypes much better accuracy and precision. The computerized process of CNC prototyping will also ensure that tight tolerances will always be achievable with this production method.
● No tooling cycle restrictions. With injection molding, the tools or molds you create will have certain restrictions on how many cycles you can use them. For low-volume production, the cycle might be around 3,000 cycles before your tools or molds break. Meanwhile, in CNC prototyping, there are no tooling restrictions, so there will be no restricted number of prototypes you can make using this prototyping method.
● Iterative design strategy. CNC prototyping supports the use of iterative design strategies, where you will make little modifications in the blueprint to create different prototype versions at a fast pace. Meanwhile, injection molding doesn’t support this iterative design strategy, as creating the mold itself will require weeks or months to complete.
Tips for the Best Results in Your Low Production Cycle with CNC Prototyping Machining
1. Simple design is preferable to keep production fast. With CNC prototyping, you can either choose to use a simple design or a complex design, and this manufacturing method can make prototypes based on whatever design you put on it. However, a simpler design means that the process won’t require too complicated steps to complete, therefore keeping the production duration fast. If you are on a tight deadline, it’s best to go for a simple blueprint design for your prototypes rather than making it complicated.
2. Keep the materials budget-friendly and available. There are various material choices you can pick for the CNC prototyping process, with each material offering you different levels and grades to match with the budget and quality you need. It’s best to keep the materials budget-friendly, as it will be a lot cheaper to produce the prototypes with them. Also, keep the primary materials you use available at all times, especially during repeated production cycles.
3. Keep a high material machinability. The machinability factor is very important for you to look for because it will determine whether your materials will be easy to work with during the CNC prototyping process. High machinability means more ease for you to cut, drill, or apply various machining processes to it. It’s best to keep a high material machinability to allow you to speed up the production process.
4. Don’t ignore the QC assessment. QC assessment is also an important factor because the prototypes or final products that have passed your QC assessment mean that they are up to your standards in quality. Don’t ignore the importance of QC assessment just because you are producing in small quantities. Fire up and improve the QC assessment to ensure that all your products or prototypes, along with the production process, always reach the threshold of your quality standards.
5. Eliminate any complicated elements in your blueprint. Your design blueprint will determine how fast or how easy the CNC prototyping process will be. Eliminating any complicated elements in your blueprint, such as by removing sharp corners, can simplify the machining process, which will in turn make the production process even faster to complete. It can also keep the quality and accuracy of your prototypes or final products at their best.
Conclusion – Following This Guide
For low-volume production, CNC prototyping is your best option to come up with the best results in your prototyping project. You can follow the tips as explained in this guide to ensure that your CNC prototyping can go smoothly.
Wir wollen Spritzgusswerkzeug herstellen lassen. Gut zu wissen, dass dies auch für die Kleinserienproduktion geeignet ist. Dies hätte ich nicht erwartet.
Hallo Laura. Danke für die Wertschätzung. Wir werden viel Wissen zum Thema Spritzgießen veröffentlichen. Bitte fügen Sie unsere Website zu Ihren Browser-Lesezeichen hinzu.