Current status and development trend of high-end CNC machine tools
High-end CNC machine tools are part of capital-intensive industries. To manufacture high-quality machine tools with consistent interchangeability of parts, machine tool companies must invest in precision equipment with accuracy levels 1-2 orders of magnitude higher than their products.
These investments should align with advanced process equipment and precision-controlled temperature and humidity workshops. This requires significant fixed-asset investment.
According to the 2022 World Machine Tool Survey by Gardner Intelligence, global machine tool output and consumption in 2022 reached €80.3 billion and €80.8 billion, respectively.
As a share of industrial and manufacturing added value, machine tool output accounted for just 0.42% and 0.72%.
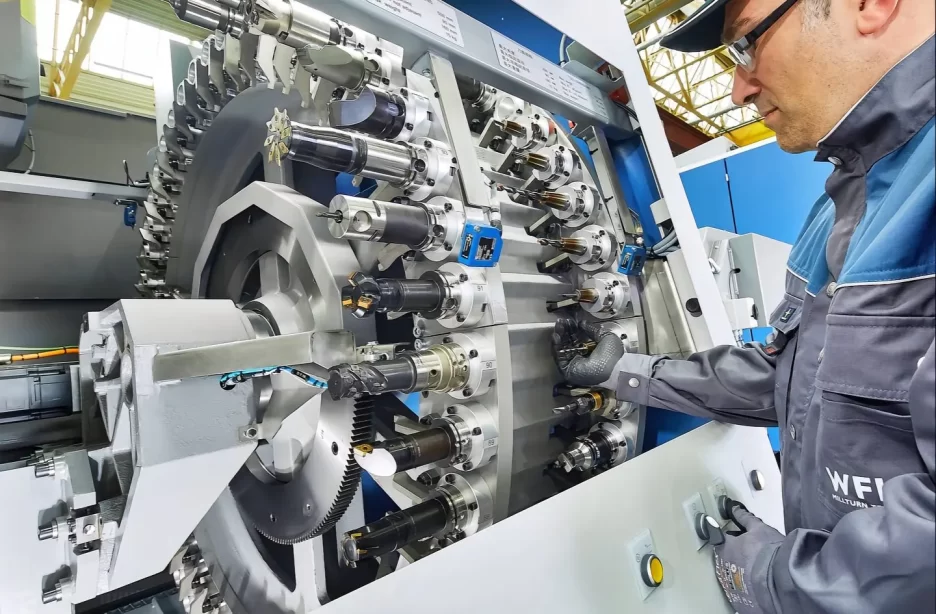

Characteristics
High-end CNC machines reflect the technological depth of a country’s manufacturing capabilities.
They are characterized by high technical requirements, niche market demand, heavy capital investment, and low returns. This field emphasizes gradual innovation and spans broad application areas.
Work methods and expertise must be incrementally solidified into software and models, with technological advancements taking up to 20 years per generation.
Well-known international CNC machine tool companies, often with a century’s history, have built core competencies through long-term technological inheritance and iteration.
Development Trends
High-end CNC machines are advancing toward higher performance, intelligence, multifunctionality, and sustainability.
High Performance
Rapid advancements in aerospace and other critical sectors and new material applications demand higher speeds, accelerations, and precision.
For example, spindle speeds now reach 15,000–50,000 rpm, table traverse speeds reach 60–200 m/min, and cutting feed rates exceed 60 m/min with accelerations of 1–5G. Automatic tool change takes just 0.5 seconds.
CNC systems now calculate and execute commands at increasing speeds, enabling high feed rates at high resolutions.
Precision levels for precision machining tools have improved to 1 μm, while ultra-precision machining has achieved nanometer-level accuracy.
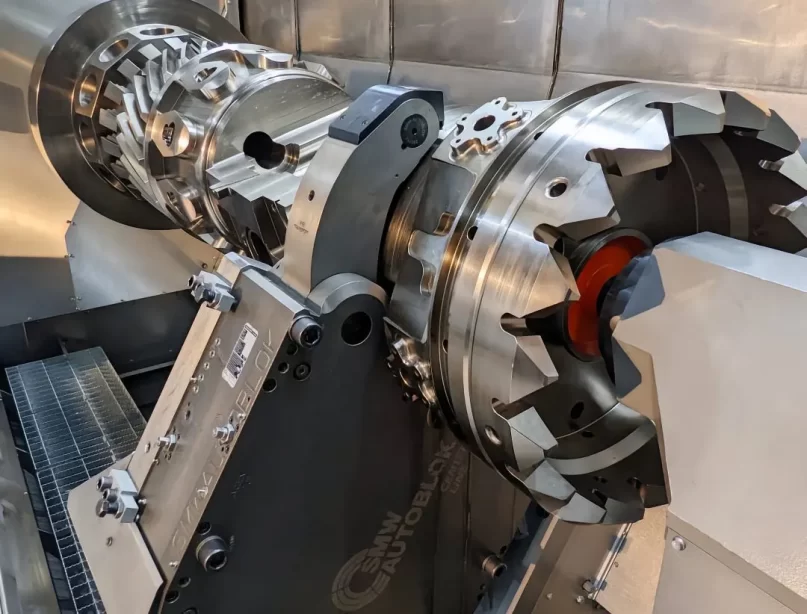
Multifunctionality
Machine tools combining various processes are used for batch production of specific products or processes, reducing manufacturing costs and improving quality and efficiency.
For example, milling-turning, turning-grinding, and forming composite machines greatly enhance accuracy and productivity.
Integrating different machining methods, such as laser or electron beam processing with traditional cutting, has become a new industrial trend.
Intelligence
High-end CNC machines are evolving from automation and digitalization to intelligence.
Integrating industrial internet, big data, and AI technologies accelerates this transition, enabling vertical integration within digital factories.
Intelligent machines can self-sense, learn, adapt, organize, and make decisions.
Real-time monitoring of equipment and products ensures flexible, automated control, marking a crucial development trend for high-end CNC machines.
Sustainability
The focus on energy consumption and sustainability in machine tools has grown significantly in recent years.
Under the “carbon neutrality” strategy, lightweight designs, eco-friendly materials, green manufacturing processes, low-carbon emission control, energy-saving measures, and energy recovery technologies have become essential.
The International Organization for Standardization (ISO) has established energy-saving standards for machine tools.
Sustainability is poised to become a competitive advantage in the future development of high-end CNC machines, playing a key role in achieving national “dual-carbon” goals.
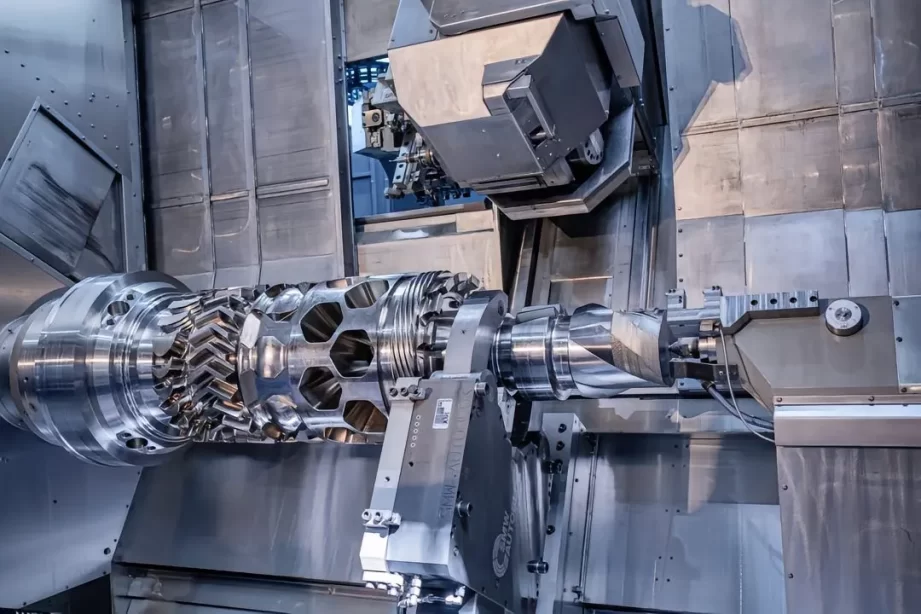
Global Development
Major countries have long recognized the strategic importance of high-end CNC machines for industrial development.
They have consistently increased support for original innovations and technological leadership in the machine tool sector to secure strategic advantages.
Leadership in Developed Countries
Developed nations like Germany, Japan, and the U.S. dominate core technologies for high-end CNC machines and continue to lead in developing next-generation intelligent manufacturing equipment.
European, Japanese, and American companies dominate the global high-end machine tool market.
Europe accounts for 30% of global production, excelling in five-axis CNC machines, composite CNC machines, and specialized equipment.
Countries like Switzerland, Italy, France, Spain, and Austria lead in various niche applications, such as aerospace manufacturing, heavy-duty machine tools, and coordinate boring machines.
Japanese CNC machine tools are primarily exported worldwide, with leading companies like Yasda, Yamazaki Mazak, Okuma, and Makino.
U.S. companies like Gleason, Ingersoll, Moore, and Hardinge maintain leadership in high-end CNC machines despite some decline.
Monopoly in Advanced CNC Systems and Core Components
Companies like Japan’s Fanuc, Germany’s Siemens, and Heidenhain dominate advanced CNC systems (including control and servo devices).
Europe and Japan also control the high-performance components market.
For example, German and Swiss companies dominate the spindle product market, fulfilling over 80% of the demand for high-end applications. In comparison, Japanese and European companies control over 90% of China’s market for high-end rolling components.
Standard and Core Technologies in High-End CNC Machines
Key technologies include design, manufacturing, assembly, functional component production, CNC systems, CAM/CAE software applications, digital precision measurement, reliability, precision maintenance, and spindle and drive transmission technologies.
Developed nations maintain their dominance through technical blockades like the Wassenaar Arrangement and mergers forming large industrial groups.
China’s Position in the CNC Machine Tool Industry
China remains the world’s largest producer and consumer of CNC machine tools, accounting for 32.8% of global production and 34.5% of consumption.
Despite a comprehensive industrial chain and product range, most Chinese companies focus on mid and low-end markets, lacking competitiveness in high-end CNC machines.