Laser Engraver Machine: Precision Engraving Made Easy
Laser engraving involves vaporizing materials to create permanent and deep marks. By using a high-powered laser beam as a chisel, layers of material are removed from the surface to create the desired design. The laser beam targets specific areas with intense energy, producing the high temperatures needed for vaporization.

Components of A Laser Engraving Machine
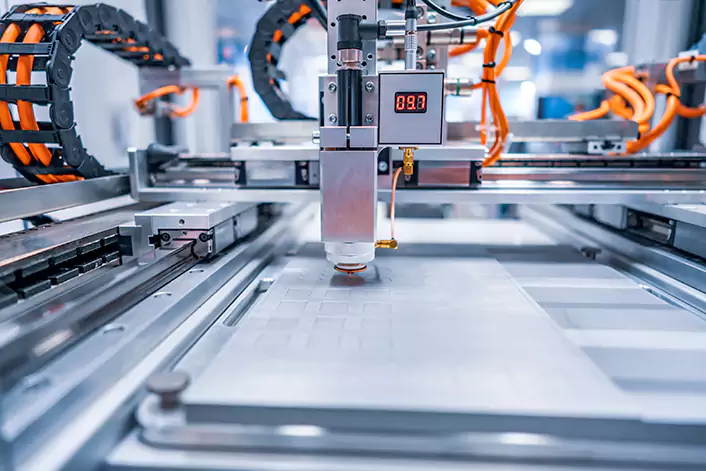

In this sense, a laser engraver machine plays a critical role in this process. Commonly, a laser engraver machine typically consists of the following components:
Laser source
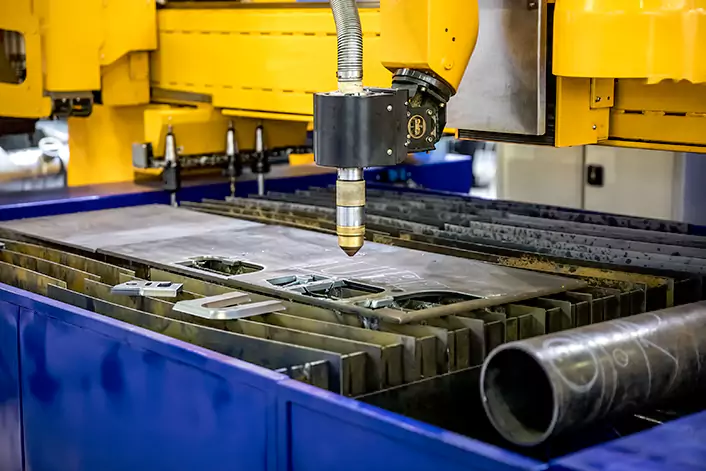

The laser source is the core component of the engraver machine, and it generates the laser beam that is used to etch or mark the material. There are two main types of laser sources used in laser engraving: CO2 lasers and fiber lasers. CO2 lasers are typically used for engraving non-metallic materials, while fiber lasers are used for engraving metals and some plastics.
Control panel and software
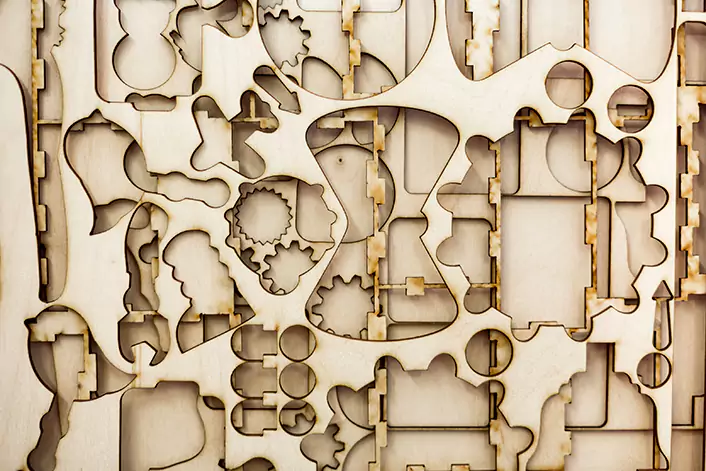

The control panel allows the user to control the laser engraver machine and adjust its settings, such as the speed and power of the laser beam. The software is used to create and upload the designs or patterns to be engraved.
Work area and bed
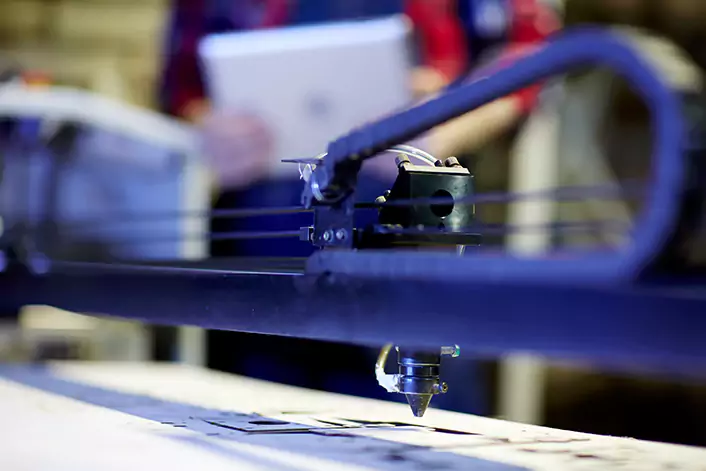
The work area is the space where the material to be engraved is placed. The bed is the surface on which the material rests, and it can be adjusted to accommodate different sizes and shapes of materials.
X-Y motion system
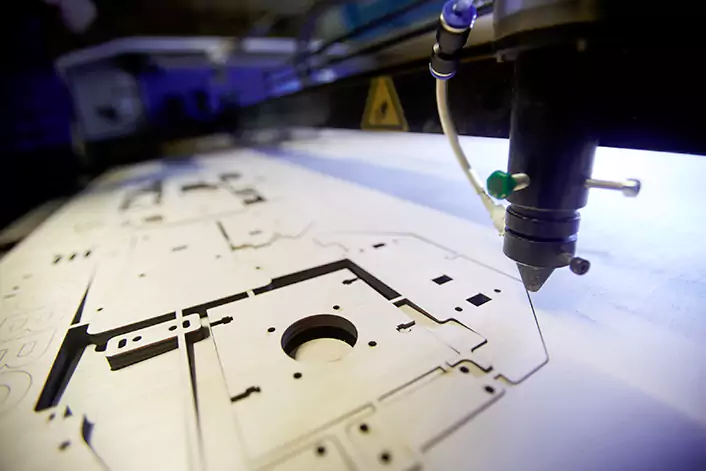
The X-Y motion system is used to move the laser head across the material to be engraved, allowing for precise and accurate positioning of the laser beam.
Fume extractor and ventilation system

Laser engraving produces fumes and smoke that can be harmful to the user’s health and the environment. The fume extractor and ventilation system help to remove these fumes and ensure the laser module is in a safe working environment.
How Laser Engraving MachineWorks

Laser engraving works by using a high-powered laser beam to etch or mark the surface of a material. The process typically involves the following steps:
Beam focusing and intensity
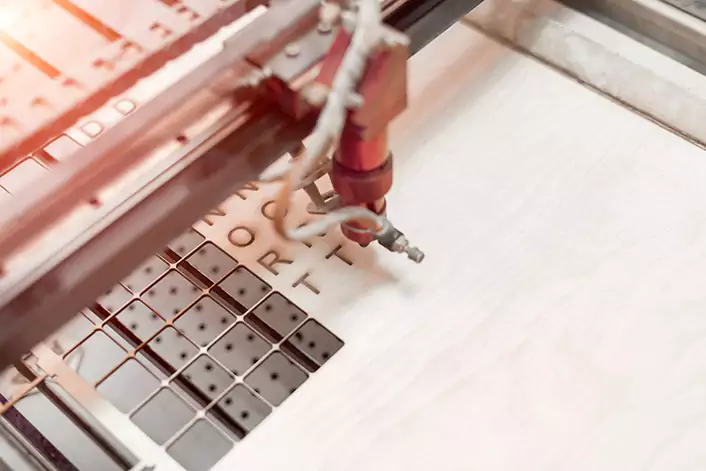
The laser beam is focused onto a small point using a lens, which increases its intensity and allows it to vaporize or melt the material.
Material absorption and melting
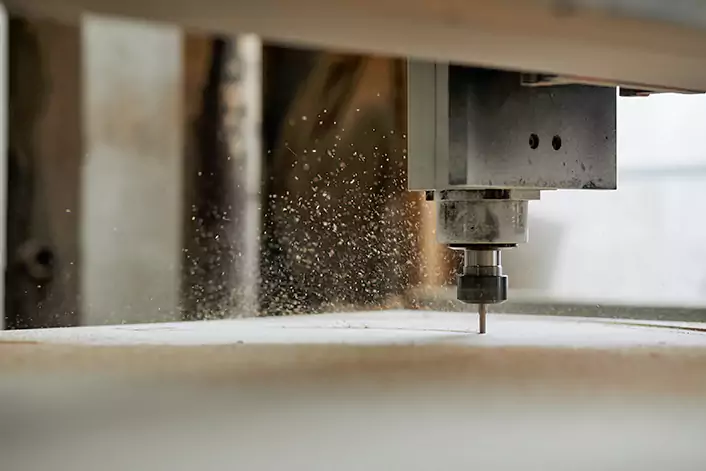

The laser beam is absorbed by the material, causing it to heat up and melt or vaporize. The material is removed by the laser beam, leaving behind an engraved pattern or design.
Etching and marking
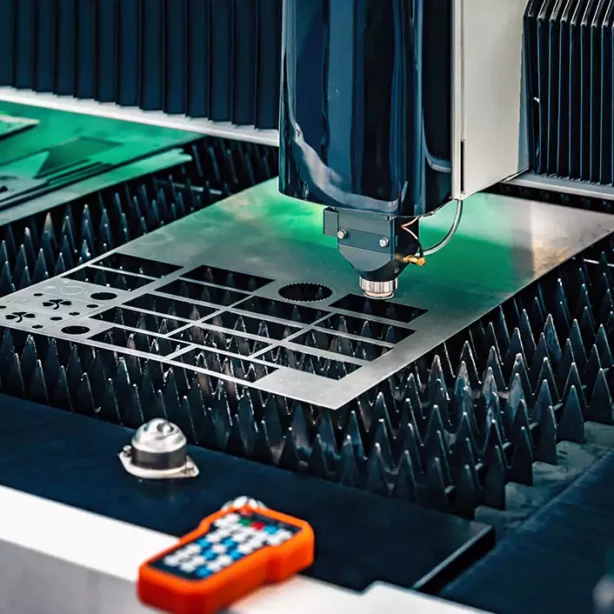

The laser beam can be used to create different effects on the material, such as etching or marking. Etching involves removing material from the surface of the material while marking involves changing the color of the material without removing any material.
The exact process of laser engraving can vary depending on the type of material being engraved, as different materials may require different laser engravers settings and techniques. For example, laser engraving metal may require a different laser source and beam intensity than engraving wood or plastic.
Overall, laser engraving is a precise and efficient process that can create intricate and detailed designs on a wide range of materials. Its versatility and precision make it a popular choice for a wide variety of applications, from personalization to industrial manufacturing.
Types of Laser Engraver Machines

There are several types of laser engraving machines available on the market, each designed for specific applications and materials. Some of the most common types of laser engraving machines include:
CO2 laser engraving machines
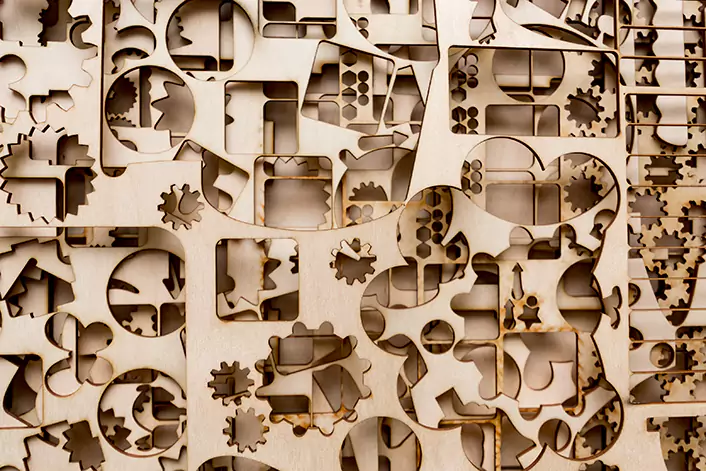

These machines use a CO2 laser source to engrave non-metallic materials such as wood, acrylic, plastic, and leather. They are commonly used for personalization, signage, and branding applications.
Fiber laser engraving machines
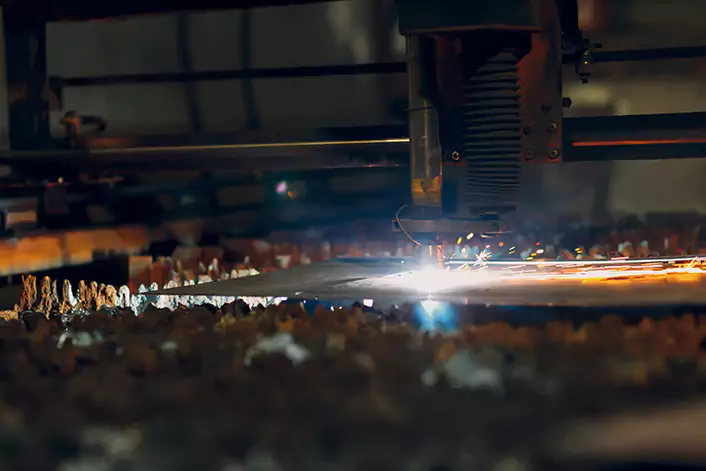

Fiber laser engraving machines are employed in the automotive, aerospace, and jewelry industries, where they utilize a fiber laser source to engrave metals such as stainless steel, aluminum, and brass.
Diode laser engraving machines
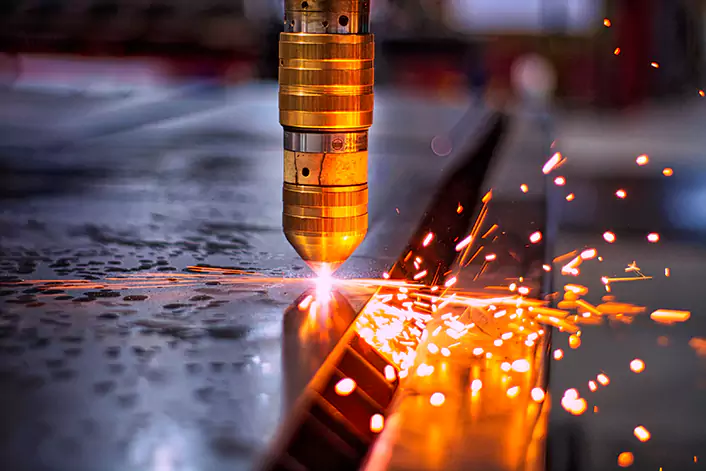

Diode laser engraving machines, which use a diode laser source, are commonly utilized in the electronics and medical industries to engrave plastics and some metals.
Green laser engraving machines

These machines use a green laser source to engrave materials such as ceramics and glass. They are commonly used in the art and jewelry industries.
UV laser engraving machines
UV laser engraving machines are frequently utilized in the electronics and medical industries to engrave materials like glass, plastics, and some metals, using a UV laser source.
Advantages of Laser Engraver Machines

Laser engraving machines offer several advantages over traditional engraving methods. Some of the key advantages include:
High precision
Laser engraving machines are capable of producing highly precise engravings, with a level of accuracy that is difficult to achieve with traditional engraving methods.
Versatility
Laser engraving machines can be used on a wide range of materials, including metal, wood, plastic, glass, and more. They can also be used to create a variety of effects, such as engraving, marking, and etching.
Speed
Laser engraving machines are typically faster than traditional engraving methods, allowing for high-volume production and quick turnaround times.
Cost-effective
Laser engraving machines can be cost-effective for both small-scale and large-scale production, as they require minimal setup time and can be operated by a single user.
Minimal material waste
Laser engraving machines produce very little waste material, as the laser beam removes only a small amount of material to create the engraving.
Disadvantages of Laser Engraver Machines
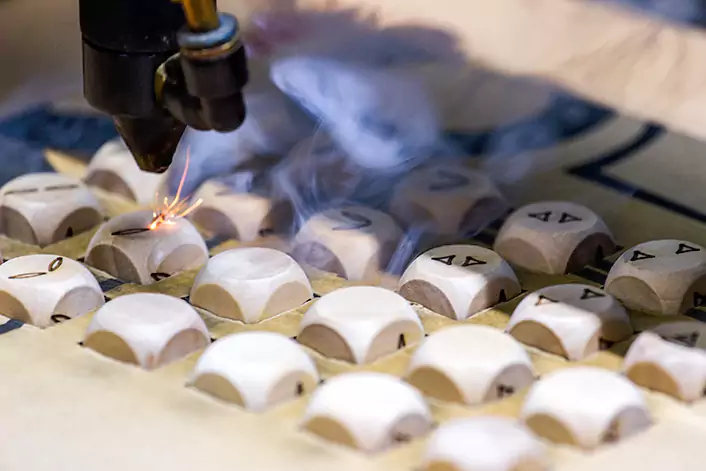

While laser engraving machines have many advantages, they also have some disadvantages that should be considered. Some of the key disadvantages include:
Limited depth
Laser engraving machines are capable of producing highly precise engravings, but they are typically limited in the depth of the engraving. This can be a disadvantage for certain applications, such as creating deep grooves or engravings.
Limited material compatibility
While laser engraving machines can be used on a wide range of materials, some materials are not suitable for laser engraving due to their composition or color. For example, transparent or reflective materials may not work well with laser engraving machines.
Risk of damage
Laser engraving machines use high-powered lasers, which can be dangerous if not used properly. There is also a risk of damaging the material being engraved if the laser is not properly calibrated or focused.
Cost
While laser engraving machines can be cost-effective for some applications, they can also be expensive to purchase and maintain. This can be a disadvantage for small businesses or individuals who have limited budgets.
Maintenance
Laser engraving machines require regular maintenance to ensure that they are operating properly and producing high-quality engravings. This can include cleaning the lenses and mirrors, replacing worn parts, and calibrating the laser.
Applications of Laser Engraving
Laser engraving has a wide range of applications across various industries. Some of the common applications of laser engraving include:
Personalization
Laser engraving can be used to personalize products, such as jewelry, phone cases, and gifts, with names, logos, or other designs.
Industrial marking
Laser engraving is often used for industrial marking on metals and plastics for identification, branding, and tracking purposes.
Signage
Laser engraving can be used to create high-quality signs for businesses, institutions, and public places.
Art and design
Laser engraving can be used to create intricate and detailed designs on a variety of materials, such as wood, acrylic, and glass.
Medical devices
Laser engraving is used in the medical industry to mark surgical instruments and medical implants with identification and tracking information.
Electronics
Laser engraving is used in the electronics industry to mark serial numbers and other information on components and devices.
Packaging
Laser engraving can be used for branding and labeling on packaging materials such as paper, cardboard, and plastics.
Future Developments and Innovations
As technology continues to advance, laser engraving machines are likely to undergo further developments and innovations. Some potential areas of development include:
Improved speed and efficiency
Laser engraving machines are already quite fast, but there is always room for improvement. Future developments may focus on improving the speed and efficiency of laser engraving machines, allowing for even faster production and higher-volume output.
Greater material compatibility
As laser technology continues to improve, it may become possible to engrave a wider range of materials with greater precision and accuracy. This could open up new possibilities for laser engraving in industries such as automotive, aerospace, and construction.
More advanced software and control systems

Future laser engraving machines may feature more advanced software and control systems that allow for greater customization and flexibility in the engraving process. This could make it easier to create complex designs and patterns with greater accuracy and precision.
Integration with other technologies
Laser engraving machines may be integrated with other technologies, such as robotics or artificial intelligence, to improve efficiency and precision in the engraving process.
3D laser engraving
As 3D printing technology continues to evolve, it may become possible to use lasers to engrave 3D objects with greater precision and accuracy. This could open up new possibilities for customization and personalization in a range of industries.
Overall, the future of laser engraving technology is likely to be characterized by continued innovation and improvement, as manufacturers and engineers seek to create faster, more precise, and more versatile engraving machines to meet the needs of a wide range of industries and applications.