Urethane Casting: What Is It and Why Chose It
Urethane resin is a versatile material used to produce a variety of plastic objects. Its applications are diverse, as it can yield both pliable, almost rubber-like products and rigid plastics.
What is Urethan Casting?
Urethane casting (or polyurethane casting, or vacuum casting) is a technique employed in the fabrication of short-run, low-volume products, such as custom-made models or movie props. The process entails pouring the urethane into a mold and allowing it to harden, but we’ll delve into the specifics later.
Urethane casting is an excellent, cost-effective means of producing both parts and entire models of high quality. It is particularly useful for intricate designs, as it produces a polished finish rapidly and at a lower cost than other methods.
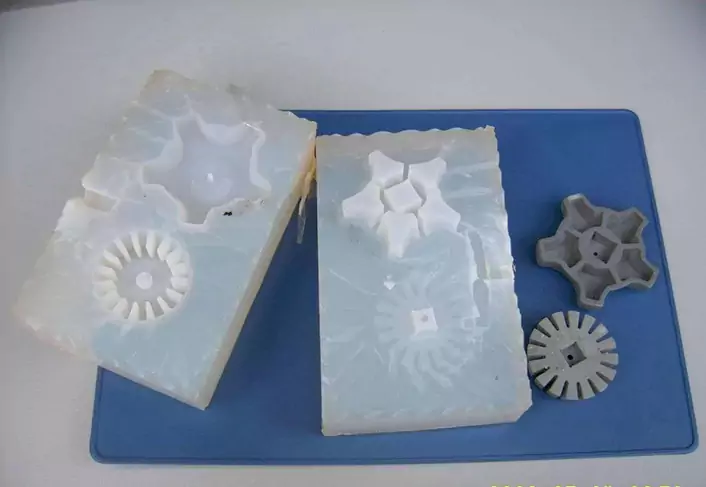

Brief History and Development
The urethane casting process originated in the mid-20th century, when polyurethane, a synthetic polymer, was first developed. The material quickly gained popularity due to its durability, flexibility, and versatility, and manufacturers began experimenting with ways to use it to create a wide variety of products.
In the early days of urethane casting, the process was primarily used to create molds for the manufacturing of polyurethane foam products such as car seats and mattresses. However, as the technology behind the process evolved, it became possible to use urethane casting to create solid plastic parts as well.
Today, the urethane casting process is widely used in industries such as aerospace, automotive, and medical devices, where high-quality, low-volume parts are needed. The process has become increasingly sophisticated over time, with advances in materials, equipment, and software allowing for greater precision and efficiency in the production of parts.
Urethane Casting Process
Urethane casting is a manufacturing process that involves pouring liquid polyurethane into a mold to create a solid, plastic part. The process is often used to create prototypes, low-volume production runs, and replacement parts for existing products.
Here are the basic steps involved in the urethane casting process:
Create a masterpiece
Depending on the nature of the design, the masterpiece can be created by CNC machining, 3D printing, or other machining processes. The masterpiece is going to be used to create mold in later procedures.
Create a mold
The mold of urethane casting can be made from metal, silicone, or even wood, but in the rapid prototyping industry, most often it is made from silicone. The liquid silicone is poured into a box with the masterpiece placed in the box. The silicone is then cured and turned from liquid to solid. The solid silicone is then cut into 2 halves, the masterpiece is removed. The cavity in the silicone mold then has the exact shape of the masterpiece.
Mix and pour the polyurethane
Before each casting, the surface of the mold cavity is covered with a release agent to avoid sticking the urethane.
The polyurethane material comes as two separate liquids, which must be mixed together in the correct proportions. The tint, if any color is required, should be mixed into the liquid too. Once the material is mixed, a chemical reaction starts which turns them into a solid piece. This is called curing, or a more fancy jargon, room temperature vulcanization. The vulcanization process could last minutes to hours depending on the specific type of polyurethane used. The mixed polyurethane resins are then poured into the mold cavity.
Vacuum chamber
It is inevitable that bobbles would be created in the polyurethane when mixing. The bobbles could affect the final product’s strength and outlook. They have to be removed. This is done by putting the mold into a vacuum chamber, where bobbles surface from the liquid by the low air pressure around the mold. That is why the urethane casting process is also called vacuum casting.
Demold the part
Once the part has cured in the mold cavity, it can be removed from the mold. Normally this just means opening the two halves of the mold and taking the product out. But if the product or the mold is complex, this step can sometimes be challenging. Once the gates and risers are cut off from the part, a perfect copy of the masterpiece shape is produced.
Finish the part
After the part has been removed from the mold, it may need to be polished or painted to achieve the desired look and feel.
The silicone mold can be used for up to about 12 ~20 castings before it has to be replaced. In urethane casting, when silicone is exposed to the resins, the chemical breakdown makes it turns hard and eventually crumble.
Equipment Required
The equipment required for urethane casting work includes:
Mixing equipment
Mixing containers, mixing sticks or paddles, and measuring tools are necessary to combine the urethane resin and any additives accurately.
Mold release agent
A spray or brush applicator is typically used to apply the release agent to the mold surface.
Vacuum chamber and pump
Optional equipment is used to remove air bubbles from the mixture and improve the quality of the final casting.
Heating equipment
In some cases, heat may be used to accelerate the curing process of the urethane material.
Personal protective equipment (PPE)
Gloves, goggles, and a respirator may be necessary to protect the caster from exposure to the urethane material and any fumes.
Mold
The object to be cast is typically made of silicone, polyurethane, or other materials.
Workbench or table
A flat and level surface is necessary to ensure that the mold and casting material remain stable during the casting process.
Clamps or weights
Used to secure production parts in the mold to the work surface and prevent any movement during the casting process.
Applications of Urethane Casting
Some applications of urethane casting include:
Prototyping
Urethane casting can be used to create prototypes of products quickly and cost-effectively. The process allows designers and engineers to test their designs and make modifications before committing to expensive tooling.

Short-run production
Urethane casting is an ideal process for producing small to medium quantities of parts. The molds used in urethane casting are durable and can produce high-quality parts for a limited production run.
Replacement parts
Urethane casting is an excellent method for producing replacement parts for machines, equipment, and other products. This process allows for a fast turnaround time and cost-effective production of parts that are no longer available or too expensive to produce using other methods.
Medical devices
Urethane casting is widely used in the production of medical devices, such as prosthetics, braces, and other orthopedic devices. The process allows for the creation of custom-fit devices that can be easily adjusted to meet the patient’s needs.
Consumer products
Urethane casting is used in the production of a wide range of consumer products, including toys, sports equipment, and household goods. The process allows for the production of high-quality products that can be customized and manufactured in small quantities.
Automotive and aerospace parts
Urethane casting is used in the production of automotive and aerospace parts, such as bumpers, spoilers, and interior components. The process allows for the creation of lightweight, durable, and high-quality parts that meet the stringent requirements of these industries.
Why Choose Urethane Casting
Some advantages of urethane casting include:
Save costs
When dozens of prototypes are required, urethane casting parts are often more cost-effective per piece than additive manufacturing. Additive manufacturing may increase the price by requiring multiple builds to produce more prototypes, while the cast urethane process can mold parts continuously.
To fabricate cast urethane pieces, silicone molds are commonly utilized. The cost of silicone molds is usually significantly lower than that of aluminum or steel tools utilized in injection molding. The molds required to produce urethane parts may range from hundreds to thousands of dollars, while injection mold tooling can range from thousands to tens of thousands of dollars.
Design Flexibility
Urethane molding employs soft tools or silicone molds to produce cast urethane pieces, enabling design changes to be implemented quickly based on customer feedback. Since silicone molds have a limited number of shots (usually 25-30 per mold), design modifications can be made from mold to mold at minimal costs. Even if a tool needs to be revised or remade, the cost is a fraction of what an injection mold tool would cost, and the lead time is halved.
Design flexibility is another advantage of this process, allowing products to incorporate features that are difficult to mold, such as undercuts, thick sections, or other elements that would not be achievable in injection molding due to the use of soft tools and thermoset materials.
With flexible and elastic molds, parts can be extracted without expensive hand loads or slides like those required in injection molding. Molds can also be created in multiple pieces that are simple to remove for releasing the part and assembling for the next shots.
Tooling Lead Time
Compared to traditional injection molding, the tooling lead time for urethane silicone mold-ing is shorter. While an injection mold tool can take four to 12 or more weeks to produce, silicone molds used in urethane casting can be completed in as little as one to two days, regardless of the part size.
Material Offerings
In urethane molding, polyurethanes are utilized to replicate the characteristics of production-grade plastic used in injection molding. Urethane casting is very often used to decide the right material to be used in later massive production.
Part Finish
Cast urethanes possess strength and surface finish that is highly comparable to injection-molded pieces. 3D printing on the other hand can not provide the same strength and surface. That is another reason that urthanes casting is used to test and decide what material to use in the massive production.
Urethane Casting Vs. Plastic Injection Molding Differences
Let’s take a closer look at some differences you should keep in mind when choosing between injection molding and urethane casting:
Upfront costs are a major consideration, with injection molds being far more expensive due to their metal construction. This makes injection molding a better option for long-term mass production, while urethane casting molds can be made much more affordably, making them ideal for one-off designs or low-volume batches.
The cost of materials is also a factor to consider. Production-grade plastics such as PVC, ABS, acetal, and LPDE are much more expensive than urethane, making urethane the better choice for prototypes and low-volume work.
Lead times for injection molding can be lengthy, sometimes taking months to create the molds. Urethane silicone molds, on the other hand, are much quicker to create, and can even be made with a 3D printer or by hand. This significantly reduces lead times, allowing for quick product delivery.
Per-part cost is typically higher for urethane casting due to the limited number of pieces that can be made with each mold. Injection molding, on the other hand, produces higher volumes, resulting in lower costs for materials and tools. Overall, injection molding is usually the most cost-effective option for long-term production.
Conclusion
In conclusion, urethane casting is a valuable alternative to plastic injection molding for small-volume production and prototyping. While it has some disadvantages such as limited material options and per-part cost, urethane casting offers benefits like faster lead times, lower upfront costs, and customizable properties. By understanding the differences between the two processes and considering the specific needs of your project, you can make an informed decision on which method is best suited for your product development and production goals.