Plastic for CNC Machining: Plastic Parts Can be Accurate Too

Plastics are a big part of the modern manufacturing industry because they are easy to find, cheap, and work well with common manufacturing methods like injection molding, 3D printing, and CNC machining. In contrast to injection molding, CNC machining is a subtractive manufacturing process that uses rotating tools and drills to shape plastic parts by taking away material from a solid block.
CNC machining is more precise for manufacturing plastic parts and compatible with a wider range of plastics than many other manufacturing methods, making it a popular choice for product teams. Currently, there are 11 commonly used plastic materials for CNC machining.
ABS Plastic
ABS is a popular engineering thermoplastic that is renowned for its impact strength, heat resistance, and machinability. Its excellent insulation properties make it ideal for electrical applications and retain its mechanical stability over time. Due to its lightweight nature, affordability, and easy availability, ABS is widely used for rapid prototyping, as well as in electronics enclosures, keyboard caps, and car dashboard components.
However, despite its strength, ABS is susceptible to wear caused by certain solvents, greases, and alcohols. Additionally, untreated ordinary ABS grades can easily catch fire and continue to burn even after removing the flame, unless they have been modified with heat stabilizers.
Benefits
ABS is an excellent choice for general-purpose prototyping, pre-molding prototypes, parts that will receive impact and require toughness, or when low cost is desired.
Drawbacks
ABS have poor abrasion or chemical resistance and will melt in acetone. It is not considered an exceptionally strong plastic material. Moreover, because of stricter environmental regulations on the West Coast of the United States, large ABS parts are only manufactured in the Midwest and on the East Coast. Consequently, the stock that is over two inches thick may take up to a week to ship, resulting in extended production time for large ABS parts.
Nylon

Polyamide (PA), also called Nylon, is a diverse range of engineering thermoplastics with excellent mechanical properties, including high impact strength, abrasion and chemical resistance, and low friction.
Among the different types of nylon, Nylon 66 stands out as an ideal choice for CNC machining due to its exceptional strength and durability, making it suitable for various applications in the automotive and medical industries. This plastic exhibits remarkable performance withstands wear and tear and resists damage caused by oil and fuel. However, Nylon 66 has low dimensional stability when exposed to moisture, and it tends to absorb moisture easily. It is also vulnerable to the effects of strong mineral acids.
Benefits
Nylon has a high strength and rigidity that it maintains over a wide temperature range, good electrical insulation, and good chemical and wear resistance. Nylon 6/6 is a good choice for applications in which strong, durable parts are needed cheaply.
When strong and durable parts are required at a reasonable cost, Nylon 6/6 is an excellent option. Meanwhile, glass-filled nylon is a material that is characterized by its rigidity, strength, hardness, toughness, and dimensional stability.
Drawbacks
Nylon 66 has a tendency to absorb moisture, which can result in swelling and a decrease in dimensional accuracy. Additionally, if there is a significant amount of asymmetric material removal during machining, the material may warp due to the internal stresses that are inherent in it.
Acrylic
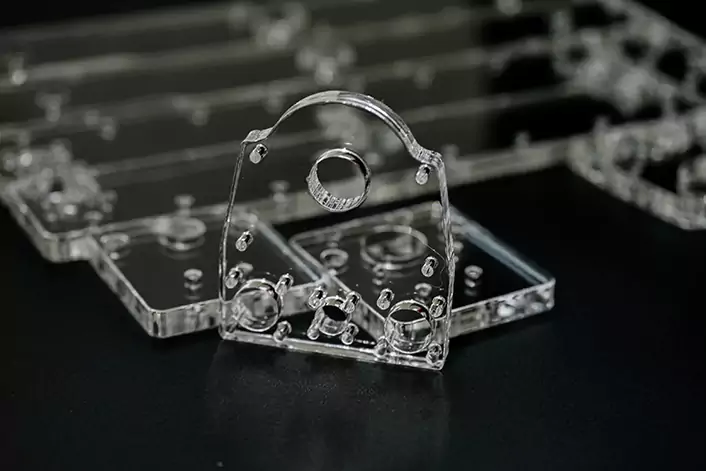

Acrylic, also referred to as PMMA (Poly Methyl Methacrylate), is a type of plastic that is commonly known by trade names such as Plexiglass or Lucite. It is a highly durable and transparent thermoplastic with decent impact strength and scratch resistance. Moreover, it is easy to glue using acrylic cement. These properties make acrylic a popular choice in a wide range of applications, such as windows, display cases, signs, aquariums, and many other consumer and industrial products.
Benefits
Acrylic is ideal for applications that require optical transparency or translucence. It can also be used as a more affordable but less durable alternative to polycarbonate. Its scratch resistance also makes it suitable for use in areas with slightly abrasive environments.
Drawbacks
Acrylic is a brittle plastic, and it has a higher likelihood of cracking or shattering instead of stretching like ductile materials. As such, the wall thickness of acrylic components should be considered, as thinner walls are more brittle.
Machined surfaces on acrylic parts lose their transparency and become frosted and translucent. To maintain transparency, it’s usually best to leave the acrylic at stock thickness. If a machined surface requires transparency, it can be polished after machining as an additional post-processing step.
Delrin/POM
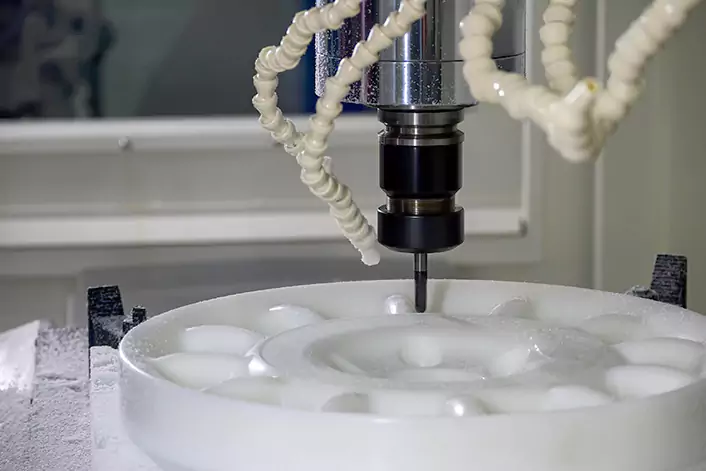

Delrin, also known as POM (Polyoxymethylene), is a highly machinable plastic commonly used in CNC machining. It is known for its exceptional strength, stiffness, and resistance to heat, wear, weather, chemicals, and fuels.
Delrin 570 and 150 are the most popular grades of POM used in CNC machining due to their excellent dimensional stability, making them ideal for creating precise parts with tight tolerances. However, POM has poor resistance to acids and can be difficult to bond. It finds applications in seat belt components, electronic cigarettes, insulin pens, and water meters.
Benefits
Delrin/POM is a reliable and durable plastic that is suitable for applications that require high stiffness, tight tolerances, or will experience a lot of friction. It has been used in commercial markets for decades due to its excellent impact, and chemical, moisture, and fatigue resistance. Additionally, it is one of the most machinable plastics, making it easy to CNC machine.
Due to its high stiffness and rigidity, Delrin/POM is an optimal choice for CNC plastic machining of parts that require tight tolerances and dimensional accuracy.
Drawbacks
Despite Delrin/POM’s desirable characteristics, such as a slippery, wear-resistant surface and excellent resistance to moisture, chemicals, and fatigue, there are some downsides to be aware of. One of the main challenges of working with Delrin is its poor adhesive properties, making it difficult to glue.
Additionally, Delrin/POM is prone to warping in areas with thin walls or uneven material removal due to inherent internal stresses. Overheating Delrin/POM beyond its maximum temperature limit can also result in hazardous off-gassing.
Polycarbonate
Polycarbonate, also known as PC, is a highly durable and transparent thermoplastic. It is one of the most commonly used materials for CNC machining and is also widely recycled globally. PC has a natural transparent milky-blue color, but it is available commercially in black as well. Both black and milky-blue polycarbonate has a glossy finish. The most common use is probably CD or VCD.
Benefits
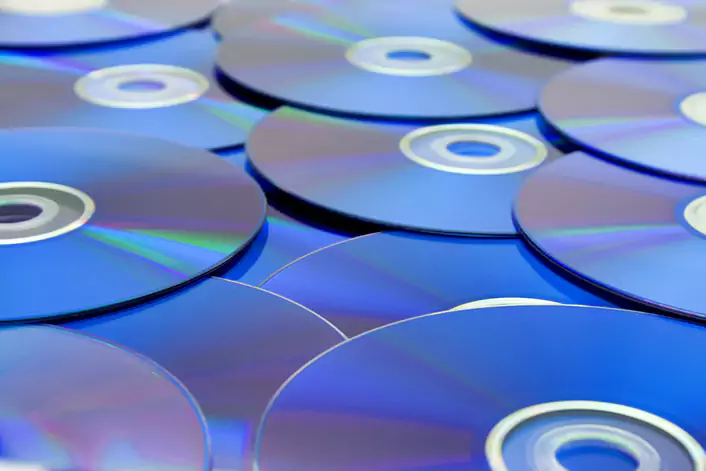

Polycarbonate is a highly impact-resistant and rigid plastic that maintains its functionality across a broad range of temperatures. It possesses optical semi-transparency, but if necessary, it can be dyed black for complete opacity. Polycarbonate is particularly suitable for situations that require a durable or sturdy plastic, or where optical clarity is necessary, which is why it is one of the most extensively employed and recycled plastics.
Polycarbonate is frequently preferred over glass as it is 250 times more resistant to impact than acrylic because it has greater toughness.
Drawbacks
Polycarbonate is susceptible to scratches and does not possess good wear resistance in its pure form. However, anti-scratch coatings and vapor polishing can be used to enhance its wear resistance or optical clarity as a post-processing step. It’s worth noting that polycarbonate is not easily obtainable in sizes greater than two inches thick, which places a limit on the size of polycarbonate parts that can be manufactured.
HDPE
HDPE, which stands for High-Density Polyethylene, is a thermoplastic that is widely used for plastic bags, bottles, pipes, and other plastic containers. It is also very common in CNC machining. HDPE possesses a naturally opaque appearance due to its crystalline structure, often with a waxy finish. However, it can also be obtained in a commercially available black-dyed finish. It is a lightweight and durable plastic with excellent chemical resistance and electrical insulation properties.
Benefits
Although it may be misleading, HDPE has the lowest density among plastics for CNC machining. Despite this, it boasts excellent chemical resistance, electrical insulation, and a smooth surface. Its low coefficient of friction, high-temperature resistance, and ability to withstand low temperatures make it a durable and cost-effective option for CNC-machined plastic parts.
Drawbacks
The primary drawback of HDPE is its weak strength, especially when subjected to tension and flexing. As a result, it is prone to stress cracking.
Conclusion
In conclusion, plastic is a versatile and popular material choice for CNC machining due to its wide range of mechanical and physical properties. Various types of plastic, such as Delrin/POM, polycarbonate, and HDPE, offer unique advantages and disadvantages depending on the intended application. Plastic parts can be just as accurate and precise as their metal counterparts, and with the right post-processing techniques, they can also have excellent surface finishes and optical clarity.
Designers and engineers should carefully consider the properties of each plastic material and choose the most appropriate one for their project. With the right choice of plastic and proper machining techniques, plastic parts can meet or even exceed the requirements of a wide range of industries and applications.
