What is the Injection Molding
Injection molding is a manufacturing process used to produce parts and products from a wide range of materials, including thermoplastics, thermosets, and elastomers. In this process, the material is melted and injected under high pressure into a mold cavity, where it solidifies and takes on the shape of the mold. The mold is then opened, and the finished part is ejected.
Injection molding is commonly used to produce plastic parts for a variety of industries, including automotive, packaging, medical, and consumer goods. The process offers high production rates, low labor costs, and the ability to produce complex geometries with high precision and repeatability.
Process
The injection molding process is a highly efficient manufacturing process used to produce a wide variety of parts and products made from various materials. It has a number of different steps, each of which is important to the whole process.
Clamping
The first stage of the injection molding process is clamping. This involves securely clamping the mold in the injection molding machine. This step is meant to make sure that the mold stays shut during the injection and cooling steps.
Injection
Once the mold is securely clamped in place, the next stage is injection. This involves melting the material and injecting it into the mold cavity under high pressure. The material fills the cavity and takes on the shape of the mold.
Cooling
After the material has been injected into the mold cavity, it needs to be cooled and solidified. The cooling stage is critical to ensure that the material sets properly and takes on the desired shape. The cooling time required depends on the material being used and the complexity of the part being produced. Usually, a water channel system is made in the mold to help shorten the cooling time.
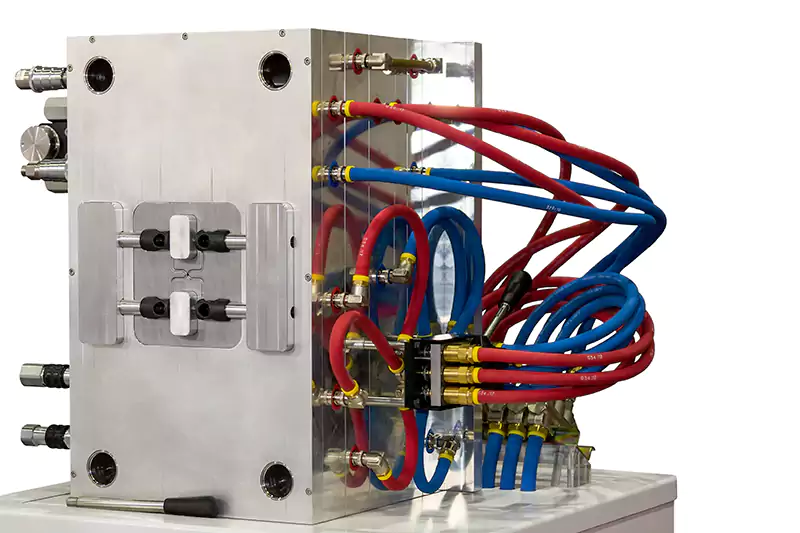
Ejection
Once the material has solidified, the mold is opened, and the finished part is ejected from the mold cavity. The ejection stage is typically done using ejector pins or plates, which push the part out of the mold cavity.
Machine
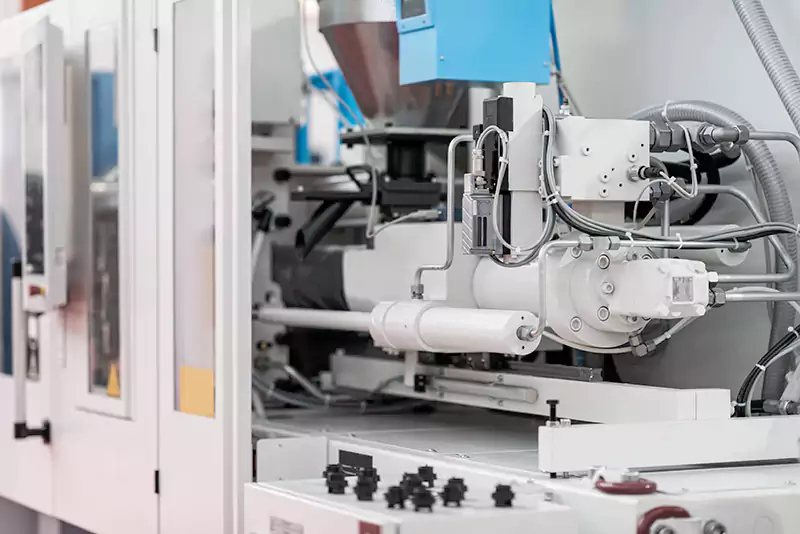
The injection molding machine is a critical component of the injection molding process, responsible for melting the material, injecting it into the mold cavity, and controlling the operating parameters to produce high-quality parts.
Types of machines
There are several types of injection molding machines, including hydraulic machines, electric machines, and hybrid machines that combine both hydraulic and electric components. The type of machine used depends on the material being used and the requirements of the specific application.
Components of the machine
The key components of an injection molding machine include the hopper, the heating element, the injection unit, the clamping unit, and the control system. The hopper holds the material and feeds it into the machine, while the heating element melts the material. The injection unit is responsible for injecting the molten material into the mold cavity, and the clamping unit securely holds the mold in place. The control system manages the overall process, including temperature, pressure, and time.
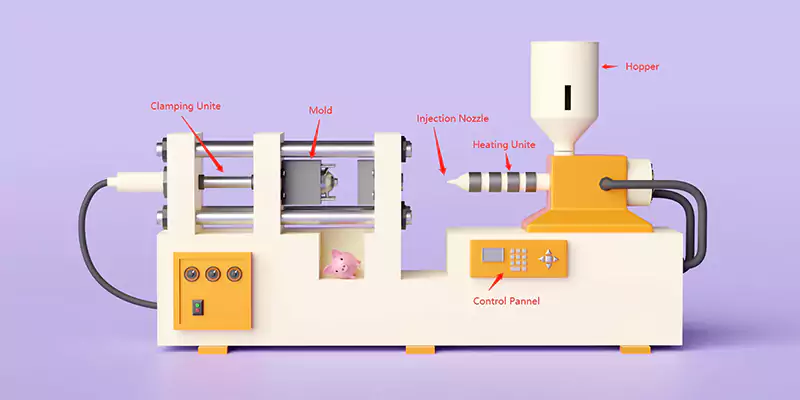
Operating parameters
The operating parameters of the injection molding machine are critical to producing high-quality parts. These parameters include temperature, pressure, injection rate, and cooling time. The machine must be calibrated and adjusted to ensure that the proper parameters are set for the specific material being used and the requirements of the application.
Applications
Injection molding is a widely used manufacturing process with a wide range of applications across many industries. Some of the most common applications of injection molding include:
Automotive
Injection molding is commonly used to produce various parts for the automotive industry, including interior and exterior trim, dashboards, and bumpers.

Consumer Goods
Injection molding is used to produce a variety of consumer goods, including toys, kitchenware, and electronic components.
Medical
Injection molding is used to produce a wide range of medical devices, including syringes, IV components, and surgical instruments.
Packaging
Injection molding is used to produce packaging materials such as caps, lids, and containers for the food and beverage industry.
Aerospace
Injection molding is used to produce parts for the aerospace industry, including interior components, structural elements, and engine parts.
Electronics
Injection molding is used to produce a wide range of electronic components, including housings for phones and computers, connectors, and switches.
Materials Used
Polyethylene (PE)
Polyethylene is a commonly used thermoplastic material that is lightweight, flexible, and has good chemical resistance. It is often used to produce bottles, packaging, and toys.
Polypropylene (PP)
Polypropylene is a thermoplastic material that is tough, durable, and has good chemical resistance. It is often used to produce automotive parts, packaging, and consumer goods.
Polystyrene (PS)
Polystyrene is a thermoplastic material that is lightweight, rigid, and has good electrical insulation properties. It is often used to produce packaging, toys, and disposable items.
Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene (ABS)
ABS is a thermoplastic material that is strong, impact-resistant, and has good heat resistance. It is often used to produce automotive parts, electronic housings, and toys.
Polyamide (PA)
Polyamide, also known as nylon, is a thermoplastic material that is strong, durable, and has good chemical resistance. It is often used to produce mechanical parts, bearings, and gears.
Polycarbonate (PC)
Polycarbonate is a thermoplastic material that is transparent, lightweight, and has good impact resistance. It is often used to produce electronic housings, automotive parts, and medical devices.
Polyethylene terephthalate (PET)
PET is a thermoplastic material that is strong, lightweight, and has good chemical resistance. It is often used to produce bottles, packaging, and automotive parts.
Pros
With injection molding, a large number of parts can be produced quickly and efficiently. After the initial costs of designing and making the molds are covered, manufacturing is very inexpensive. As more parts are produced, production costs drop.
It is also worth mentioning that injection molding produces minimal waste when compared to traditional manufacturing processes, such as CNC machining, which is characterized by cutting away excess materials. Despite this, injection molding also produces some waste, mainly from the sprue, the runners, the gate locations and any overflow material that leaks out of the part cavity (also known as flash in injection molding).
The final advantage of injection molding is that it allows for the production of many identical parts, which in turn allows for part consistency and reliability in high volume production.
Cons
It is true that injection molding has many advantages, but it also has a number of disadvantages that need to be taken into account.
There can be high upfront costs associated with plastic injection molding, particularly when it comes to tooling. In order to be able to produce any parts, you first need to create a prototype part before you can produce any parts. After this is completed, a prototype mold tool needs to be created and tested. Completing all of this takes time and money.
Large parts cannot also be produced as a single piece using injection molding. Mold tools and injection mold machines have size limitations. Injection molding machines are capable of producing smaller items, but larger items will need to be created as multiple parts in order to be able to join them together later on in the process.
One more disadvantage of large undercuts is that they are difficult to avoid without the assistance of experienced designers and can increase the cost of your project as well.
When is it Used?
When a repeatable plastic manufacturing process is needed, injection molding is usually the best option. Among their products are wire spools, packaging, bottle caps, toys, combs, musical instruments (and their components), chairs, small tables, storage containers, mechanical parts, and automotive components.
Injection molding is one of the most commonly used methods for manufacturing plastic parts, particularly when it comes to large quantities.
Is it Environmentally Friendly?
Due to improved machinery and thermosetting polymers, injection molding is becoming more environmentally friendly.
It is true that there is some material waste associated with injection molding, but it is far smaller than the waste associated with many other manufacturing processes. The exact materials used have also a bearing on the environment regarding how long they last, whether they can come from recycled materials, how they are disposed of, and of course how they are recycled. A number of factors need to be considered as well, including the lifetime of the products that are created, including their carbon footprint during their manufacturing process.
Modern injection molding machines use 20 to 50% less energy than they did ten years ago due to technological advancements.
Is it Expensive?
Molding costs are correlated with the number of cavities in the mold. Fewer cavities require less tooling work, which lowers the manufacturing costs to create an injection mold. Surface finishing, tolerance, threads, detailing, and the number of undercuts all affect a part’s cost. Added details such as these will increase the cost, as they require more tooling.
A rubber injection molding process produces durable products at a low cost. Moreover, consistent vulcanization processes with precise temperature controls can reduce waste material costs.
How much does it Cost?

The following formula can be used to calculate the exact cost of injection molding:
mold Price = material costs + design + process and profit + VAT + try out costs + packing and shipping costs.
Within these costs, materials, and parts equal around 15-30% of the total, and process and profit equal 30-50%.
Based on these factors, a small single cavity injection mold costs between $1,000 and $5,000. Molds that are larger or more complex can cost $80,000 or more. However, on average, a typical mold costs around $12,000.
Mold tools are expensive, but molding production is relatively inexpensive.
Conclusion
There are many applications for injection molding in manufacturing, particularly when producing high-volume parts. The cost of tooling and molding can be high, but the cost of production is low once this is complete. Material types ranging from metals to plastics can be molded using injection molding to produce near-identical parts.