Blow Molding: What is it? How does it work?
Overview of Blow Molding
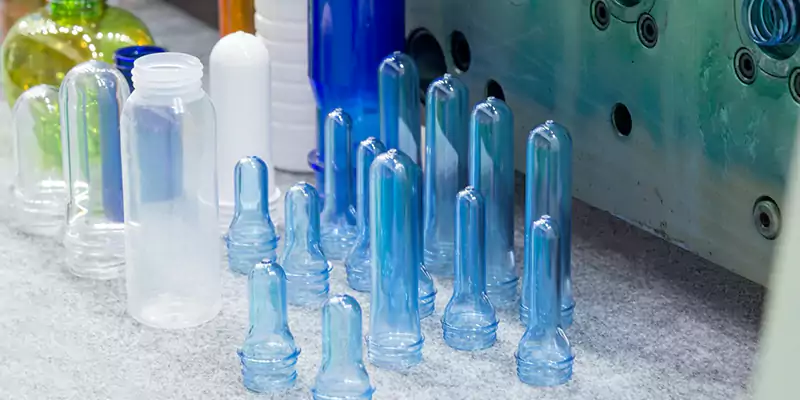

Blow molding is a plastic-forming process that creates hollow products using thermoplastic materials. The process begins by heating and inflating a plastic tube called a parison or preform. The parison is placed between two dies that determine the shape of the final product. Air is then supplied to expand the tube and form it into the mold’s shape while thinning the walls. After the blowing process, the product is cooled, ejected, trimmed, and prepared for secondary processing.
Blow molding has many applications, with bottling and packaging being the most common, accounting for about 49% of the global molding market share. Other industries that use this process include building and construction, consumer products, and transportation.
In 2019, the global molding market was estimated at around $78 billion and is projected to grow annually by 2.8% from 2020 to 2027. Polyethylene (PE), polyethylene terephthalate (PET), and polypropylene (PP) are some of the typical raw materials used in the blow molding processes.
History of Blow Molding
Blow molding is a manufacturing process used to create hollow plastic parts. The process involves heating or melting plastic resin and shaping it into a hollow form using air pressure. The history of blow molding dates back to the 19th century, with the first recorded use of blow molding in the glass industry. However, it wasn’t until the mid-20th century that the process was applied to plastics.
In 1938, the first patent for a blow molding process was filed by an American inventor, James Hendry. The process involved extruding a parison (a tube of plastic) and inflating it into a blow molding machine to create a hollow object. This process was known as extrusion blow molding and is still widely used today.
In the 1950s, the development of injection molding allowed for the mass production of more complex shapes. This process involves injecting plastic into a core pin, which is then transferred to a blow mold to create the final shape.
Stretch blow molding was developed in the 1970s, allowing for the creation of PET bottles with high clarity and strength. This process involves stretching the plastic preform before inflating it into a mold, creating a strong and lightweight plastic bottle part.
Over the years, blow molding technology has continued to improve, with advancements in materials, machinery, and automation. Today, the molding is used to produce a wide range of products, from packaging and automotive parts to toys and medical equipment.
The Blow Molding Process
The blow molding process is a manufacturing method used to produce hollow plastic parts, such as bottles, containers, and automotive parts. The process involves several steps:
Plastic resin feeding or charging
The first step involves feeding plastic resin pellets into a hopper, which then moves the pellets into the barrel of an extruder. The pellets are usually made of a thermoplastic polymer, such as polyethylene, polypropylene, or PET.
Plasticizing or melting
The plastic pellets are melted and mixed by the screw in the barrel of the extruder. The melted plastic is then forced through a die to form a hollow tube called a parison. Alternatively, in injection blow molding, a preform is injected into a mold and then inflated to form the final product.
Parison extrusion or preform injection
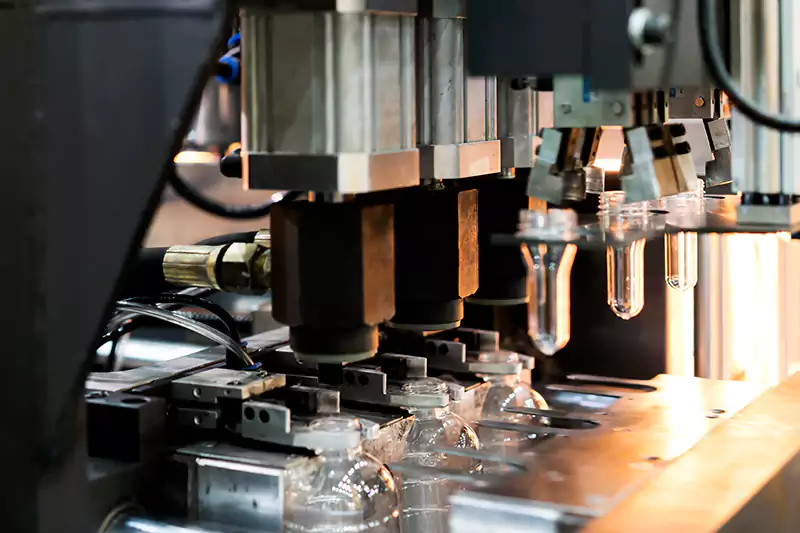

The parison or preform is extruded or injected into a two-part mold, which is then closed by a clamping unit. The mold is designed to form the plastic into the desired shape.
Sealing or clamping
Once the blow molding machine is closed, the plastic is sealed inside it. The clamping unit holds the mold tightly closed during the blow molding process to prevent any leaks or deformation of the plastic.
Inflation or blow molding
Compressed air is blown into the parison or preform, which inflates it and stretches it to the shape of the mold. The plastic is then cooled by the mold to set its shape.
Cooling and ejecting
After the plastic has been shaped, the mold is cooled to solidify the plastic. The mold is then opened, and the finished part is ejected from the empty mold cavity.
Trimming
The excess plastic, called flash, is trimmed from the finished part. This ensures that the part has a clean and consistent appearance.
Leak test
The finished product is tested for leaks or defects to ensure that it meets the required quality standards.
Blow Molding Types
There are three main types of blow molding: extrusion blow molding, injection blow molding, and stretch blow molding. Here’s a brief overview of each type:
Extrusion blow molding
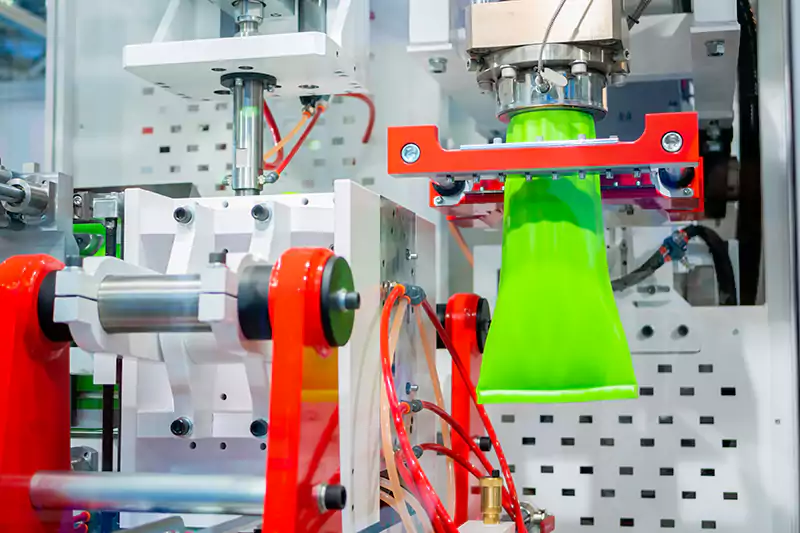

The extrusion blow molding process is the most common type of plastic blow molding used for the production of bottles, containers, and other hollow objects. The process involves melting plastic resin and extruding a parison (a tube of molten plastic) into a mold. The mold is then closed, and the air is blown into the parison, forcing it to take the shape of the mold.
Injection blow molding
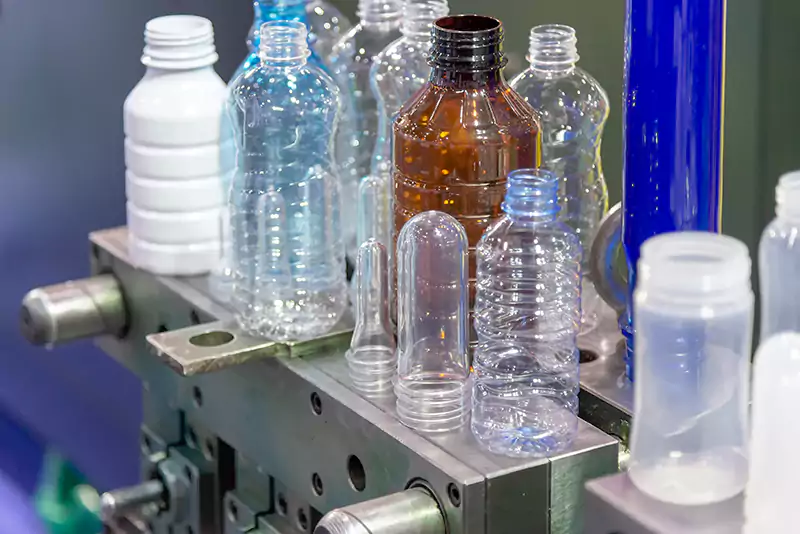

Injection blow molding is used to produce more complex shapes, such as medical vials or small cosmetic containers. The process involves injecting molten plastic into a core pin, the core pin and the injection molded plastic is then transferred to a blow mold. The core pin is removed, and the air is blown into the plastic, forcing it to take the shape of the mold.
Stretch blow molding
Stretch blow molding, also known as injection stretch blow molding, is used to produce high-quality bottles, such as those used for carbonated beverages. The process involves stretching a preform (a small plastic tube) in two directions, then inflating it into a mold. This stretching process creates a strong and lightweight bottle.
Types of Blow Molded Plastic
There are several types of plastic resins that are commonly used in blow molding. The choice of resin depends on the application and the desired properties of the final product. Here are some of the most common types of blow-molded plastics:
High-Density Polyethylene (HDPE)
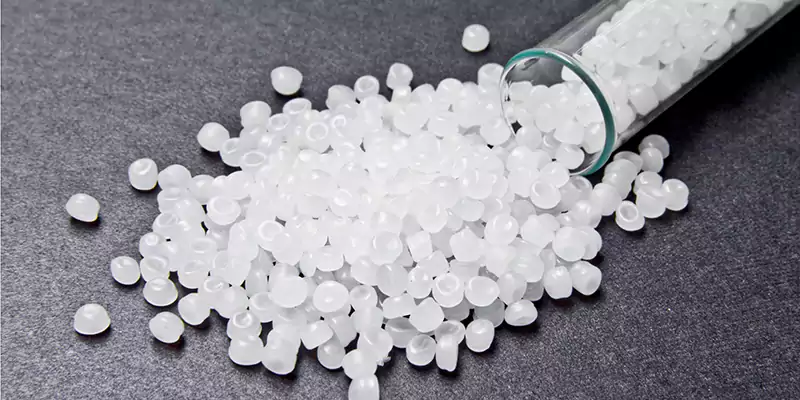

High-Density Polyethylene (HDPE) is a type of polyethylene with a high density, which results in a hard, strong, and durable material that is resistant to impact and chemicals.
Low-Density Polyethylene (LDPE)
Low-Density Polyethylene (LDPE) is a type of polyethylene with a lower density, which results in a more flexible and pliable material compared to other forms of polyethylene, such as High-Density Polyethylene (HDPE).
Polypropylene (PP)
Polypropylene is a versatile polymer that can exhibit a wide range of properties based on factors such as its molecular weight, crystalline structure, morphology, copolymerization, and the presence of additives.
High crystallinity versions of PP can offer increased tensile strength and hardness, which is comparable to HDPE, along with the ability to withstand high temperatures without loss of strength or degradation. However, PP is vulnerable to UV degradation and oxidation, which are its primary drawbacks.
Polyethylene Terephthalate (PET)
Biaxially oriented PET, commonly known as PET, is renowned for its excellent resistance to carbon dioxide permeation, making it an ideal material for the production of plastic bottles often used in carbonated beverage packaging. However, PET has a drawback in that it is prone to water absorption, which can create processing challenges since the resin must be dried before extrusion.
Why We Use Blow-Molding processes

There are several advantages of using blow-molded plastics, including:
Cost-effective
Blow molding is a highly efficient and cost-effective manufacturing process that can produce large quantities of plastic products quickly and at a low cost.
Versatility
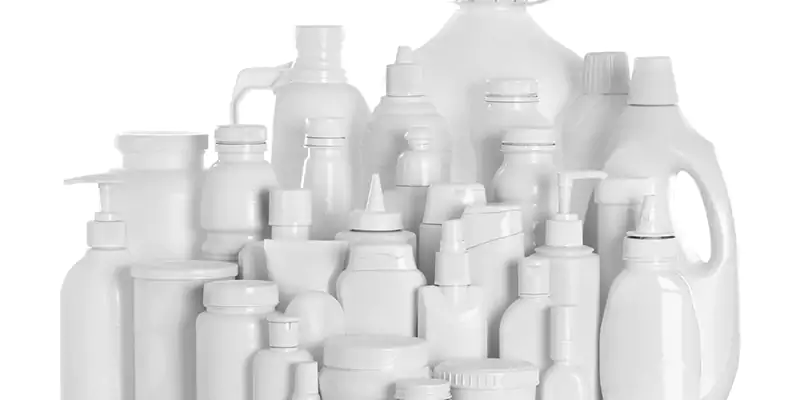

The molding can be used to produce a wide range of products in different shapes and sizes, including bottles, containers, and automotive parts.
Lightweight
Blow-molded products are lightweight, which makes them ideal for use in products that require portability and ease of handling, such as packaging materials and toys.
Durability
Blow-molded products are highly durable and resistant to impact, chemicals, and weathering, which makes them suitable for use in harsh environments.
Customization
Blow molding allows for the customization of products with different colors, textures, and designs, which helps to create unique and appealing products.
Recyclability
Most blow-molded products can be recycled, which reduces waste and conserves natural resources.
Where Can We Use It
Blow-molded plastics are widely used in various industries and applications, some of which include:
Packaging
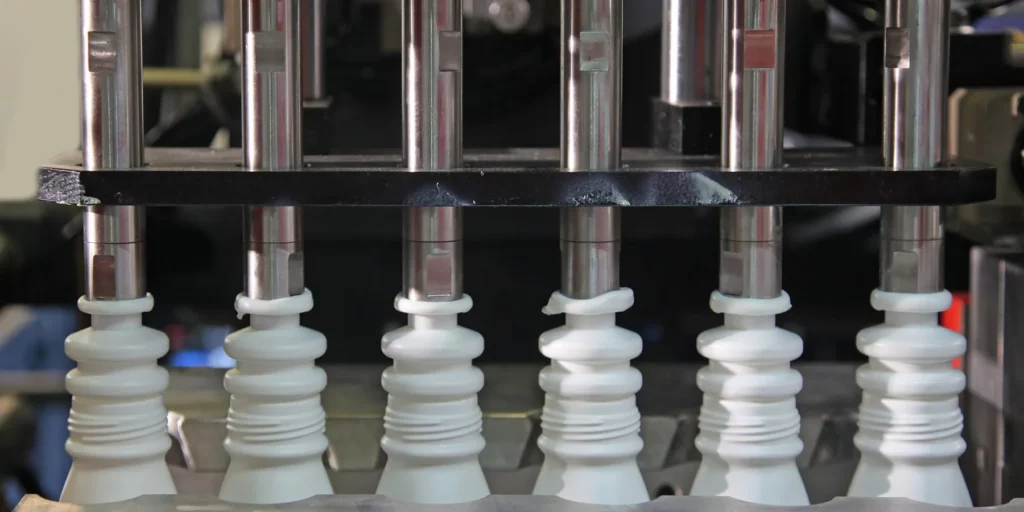
Blow-molded plastics are commonly used to produce bottles, containers, and other packaging materials for food, beverages, and other consumer products. These products offer a high level of durability, strength, and design flexibility, making them ideal for use in a wide range of packaging applications.
Automotive industry
Blow-molded plastics are used to manufacture various automotive components such as fuel tanks, air ducts, and interior parts. These products offer excellent durability, strength, and resistance to impact and temperature fluctuations, making them ideal for use in the automotive industry.
Toys and sports equipment
Blow-molded plastics are used to manufacture a wide range of toys and sports equipment, including balls, sleds, and other outdoor play equipment. These products offer a high level of durability, flexibility, and design flexibility, making them ideal for use in a wide range of applications.
Medical equipment
Blow-molded plastics are used to manufacture various medical components such as IV bags, drug delivery systems, and other medical equipment. These blow-molded products offer a high level of durability, flexibility, and resistance to chemicals and sterilization methods, making them ideal for use in the medical industry.
Construction materials
Blow-molded plastics are used to manufacture various construction materials such as drainage pipes, gutter systems, and other building components. These products offer excellent durability, strength, and resistance to weathering and corrosion, making them ideal for use in the construction industry.
Challenges of Blow Molding
Despite the numerous advantages of the molding, there are also some challenges associated with this manufacturing process, including:
Environmental concerns
One of the most pressing challenges associated with blow-molded plastics is environmental concerns. The production of plastics generates significant amounts of waste and pollution, and improper disposal of these materials can have serious consequences for the environment. Recycling is one solution to this problem, but not all types of plastics can be easily recycled, and the cost of recycling can be prohibitive for some manufacturers. Improving waste management practices and finding innovative ways to recycle and reuse plastic materials are critical steps in reducing the environmental impact of blow-molded plastics.
Limited color options
Another challenge associated with blow-molded plastics is the limited color options available for these materials. The manufacturing process can make it difficult to achieve certain colors and shades, which can be a limitation for manufacturers who want to create products with specific aesthetic or branding requirements. Some manufacturers may turn to other materials or processes to achieve their desired color scheme, which can increase costs and complexity.
Complex shapes
Complex shapes are also a challenge for blow-molded plastics. While this process is well-suited for producing simple, symmetrical shapes, it can be more difficult to achieve complex, irregular shapes. This is because the process relies on the use of molds, and creating molds for complex shapes can be expensive and time-consuming.
High production costs
Finally, high production costs for small quantities can also be a challenge for manufacturers using blow-molded plastics. The specialized equipment and tooling required for this process can make it prohibitively expensive for small-scale production runs. This can limit the ability of small businesses to use blow-molded plastics in their products and can result in higher costs for consumers.
Conclusion
In conclusion, blow-molded plastics play a crucial role in many industries, and the benefits they offer will continue to drive demand for this material. By addressing the challenges associated with the manufacturing process and developing more sustainable practices, the industry can continue to grow and thrive while minimizing its environmental impact.
Thanks for sharing such a nice blog with complete information, we are looking forward to see more blogs in future.
Hi Allied, We will hold the line that continous refresh our blog.